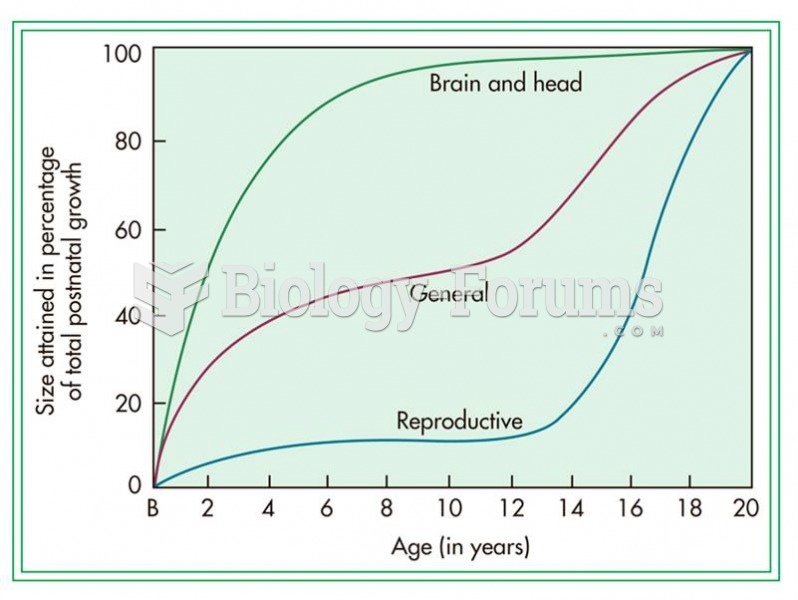
|
|
|
IgA antibodies protect body surfaces exposed to outside foreign substances. IgG antibodies are found in all body fluids. IgM antibodies are the first type of antibody made in response to an infection. IgE antibody levels are often high in people with allergies. IgD antibodies are found in tissues lining the abdomen and chest.
The term pharmacology is derived from the Greek words pharmakon("claim, medicine, poison, or remedy") and logos ("study").
Egg cells are about the size of a grain of sand. They are formed inside of a female's ovaries before she is even born.
After a vasectomy, it takes about 12 ejaculations to clear out sperm that were already beyond the blocked area.
In ancient Rome, many of the richer people in the population had lead-induced gout. The reason for this is unclear. Lead poisoning has also been linked to madness.