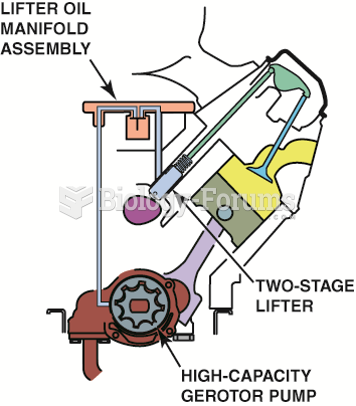
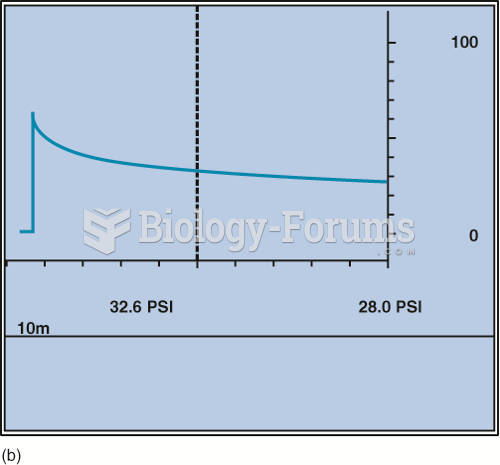
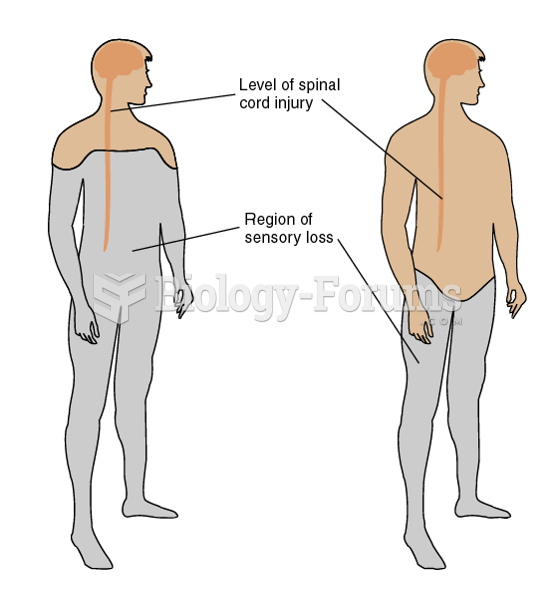
|
|
|
The human body's pharmacokinetics are quite varied. Our hair holds onto drugs longer than our urine, blood, or saliva. For example, alcohol can be detected in the hair for up to 90 days after it was consumed. The same is true for marijuana, cocaine, ecstasy, heroin, methamphetamine, and nicotine.
Amphetamine poisoning can cause intravascular coagulation, circulatory collapse, rhabdomyolysis, ischemic colitis, acute psychosis, hyperthermia, respiratory distress syndrome, and pericarditis.
Fungal nail infections account for up to 30% of all skin infections. They affect 5% of the general population—mostly people over the age of 70.
The lipid bilayer is made of phospholipids. They are arranged in a double layer because one of their ends is attracted to water while the other is repelled by water.
Inotropic therapy does not have a role in the treatment of most heart failure patients. These drugs can make patients feel and function better but usually do not lengthen the predicted length of their lives.