This topic contains a solution. Click here to go to the answer
|
|
|
Did you know?
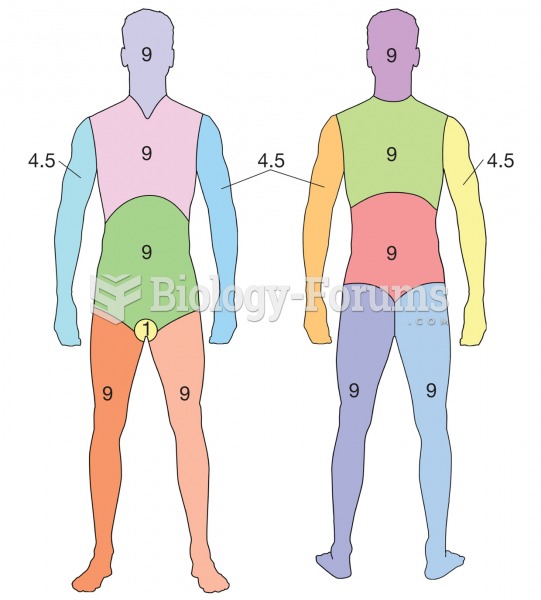
There are 20 feet of blood vessels in each square inch of human skin.
Did you know?
Most childhood vaccines are 90–99% effective in preventing disease. Side effects are rarely serious.
Did you know?
There are approximately 3 million unintended pregnancies in the United States each year.
Did you know?
Normal urine is sterile. It contains fluids, salts, and waste products. It is free of bacteria, viruses, and fungi.
Did you know?
Giardia is one of the most common intestinal parasites worldwide, and infects up to 20% of the world population, mostly in poorer countries with inadequate sanitation. Infections are most common in children, though chronic Giardia is more common in adults.