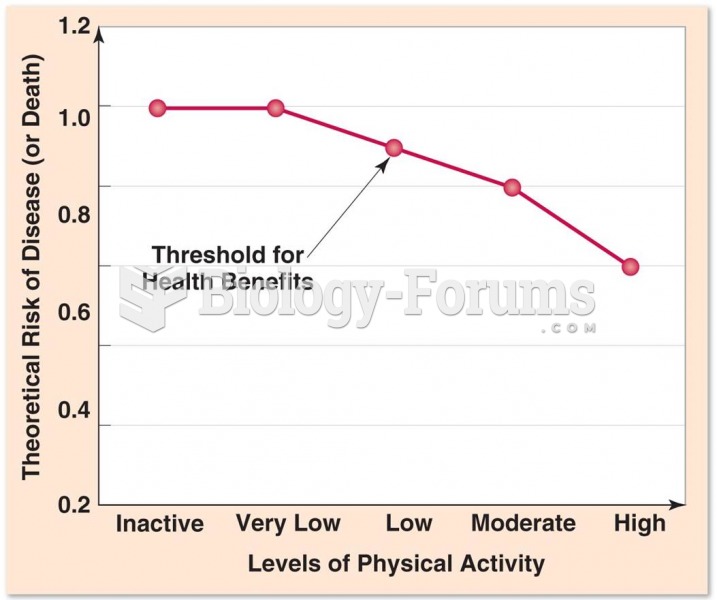
|
|
|
Certain topical medications such as clotrimazole and betamethasone are not approved for use in children younger than 12 years of age. They must be used very cautiously, as directed by a doctor, to treat any child. Children have a much greater response to topical steroid medications.
Acetaminophen (Tylenol) in overdose can seriously damage the liver. It should never be taken by people who use alcohol heavily; it can result in severe liver damage and even a condition requiring a liver transplant.
Vital signs (blood pressure, temperature, pulse rate, respiration rate) should be taken before any drug administration. Patients should be informed not to use tobacco or caffeine at least 30 minutes before their appointment.
According to the FDA, adverse drug events harmed or killed approximately 1,200,000 people in the United States in the year 2015.
There are approximately 3 million unintended pregnancies in the United States each year.