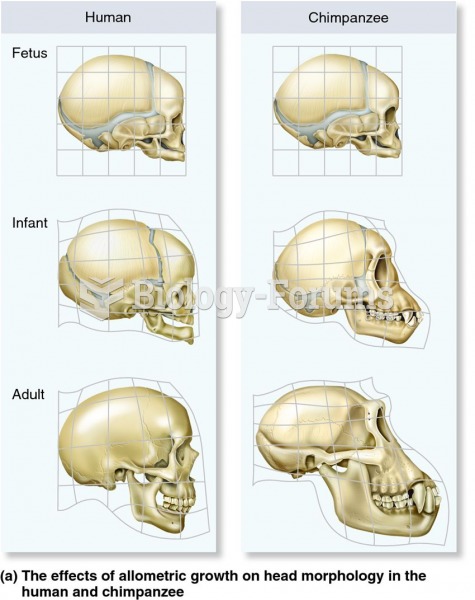
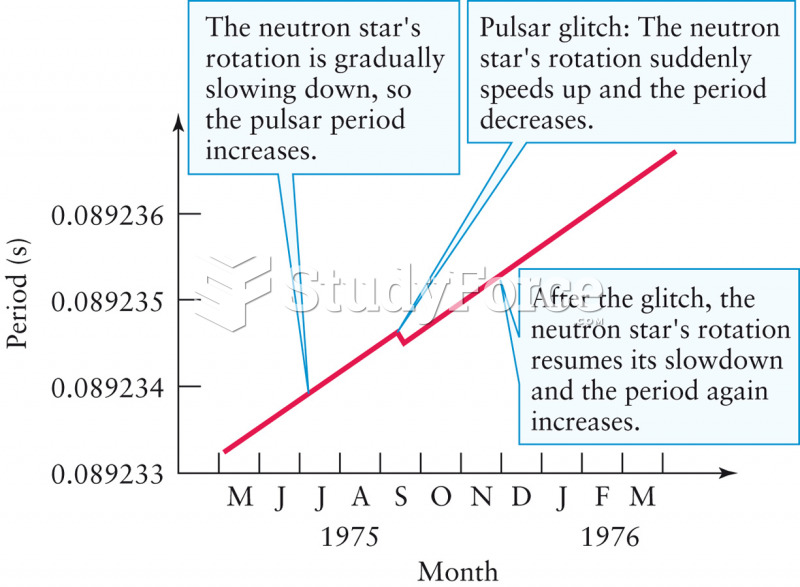
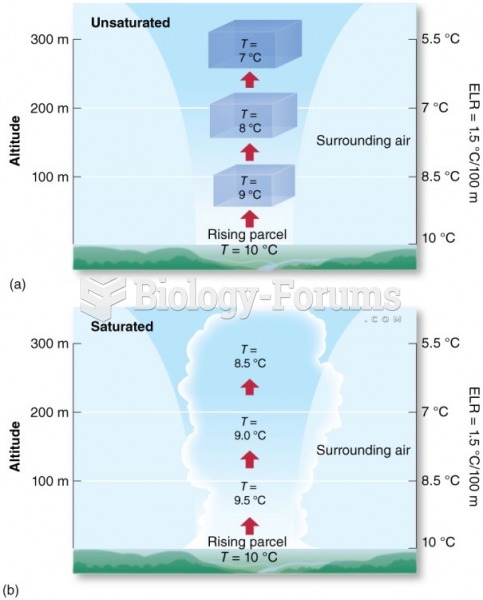
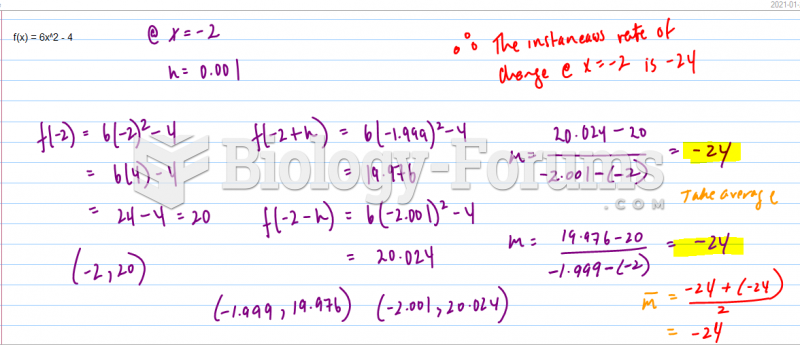|
|
|
Most childhood vaccines are 90–99% effective in preventing disease. Side effects are rarely serious.
For pediatric patients, intravenous fluids are the most commonly cited products involved in medication errors that are reported to the USP.
In women, pharmacodynamic differences include increased sensitivity to (and increased effectiveness of) beta-blockers, opioids, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, and typical antipsychotics.
The oldest recorded age was 122. Madame Jeanne Calment was born in France in 1875 and died in 1997. She was a vegetarian and loved olive oil, port wine, and chocolate.
Eating food that has been cooked with poppy seeds may cause you to fail a drug screening test, because the seeds contain enough opiate alkaloids to register as a positive.