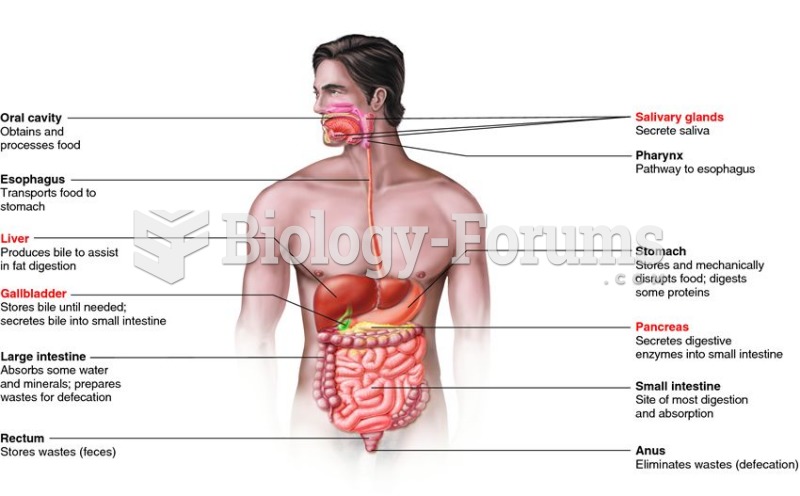
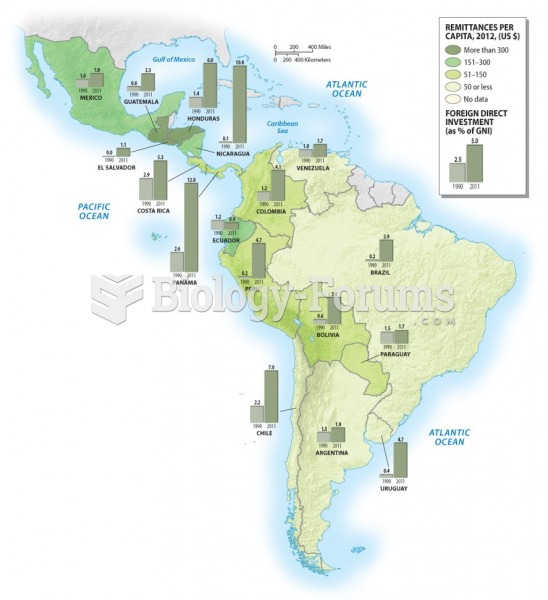
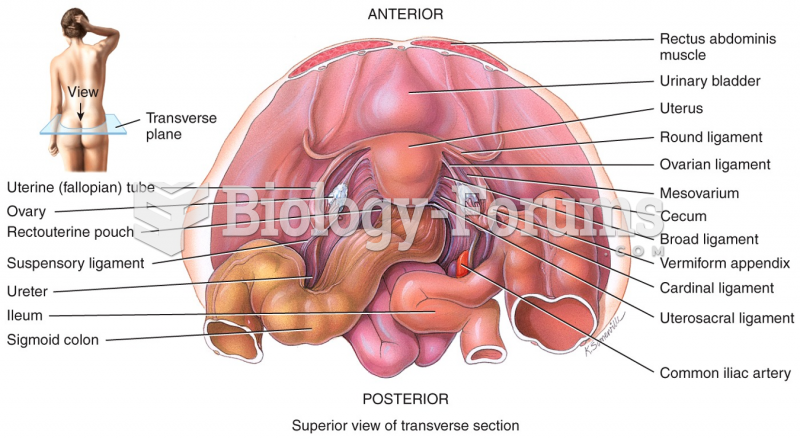
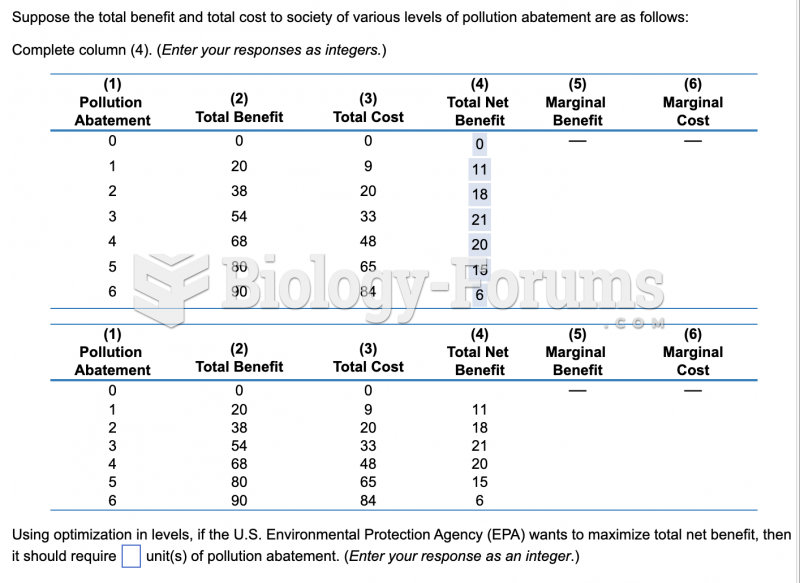
|
|
|
A cataract is a clouding of the eyes' natural lens. As we age, some clouding of the lens may occur. The first sign of a cataract is usually blurry vision. Although glasses and other visual aids may at first help a person with cataracts, surgery may become inevitable. Cataract surgery is very successful in restoring vision, and it is the most frequently performed surgery in the United States.
Street names for barbiturates include reds, red devils, yellow jackets, blue heavens, Christmas trees, and rainbows. They are commonly referred to as downers.
Never take aspirin without food because it is likely to irritate your stomach. Never give aspirin to children under age 12. Overdoses of aspirin have the potential to cause deafness.
According to the CDC, approximately 31.7% of the U.S. population has high low-density lipoprotein (LDL) or "bad cholesterol" levels.
Though “Krazy Glue” or “Super Glue” has the ability to seal small wounds, it is not recommended for this purpose since it contains many substances that should not enter the body through the skin, and may be harmful.