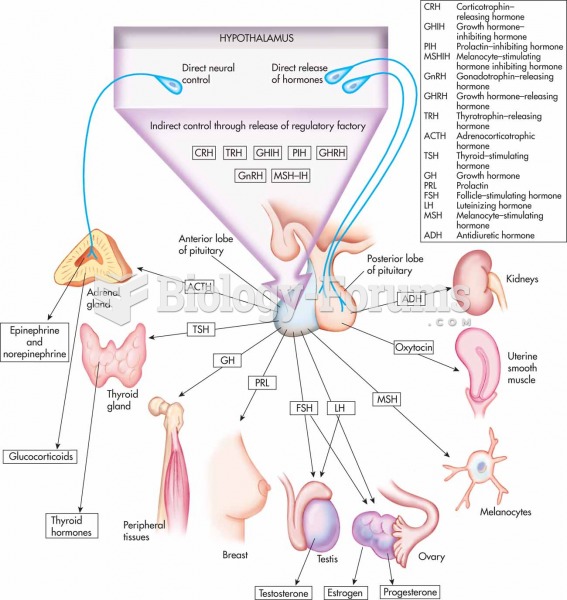
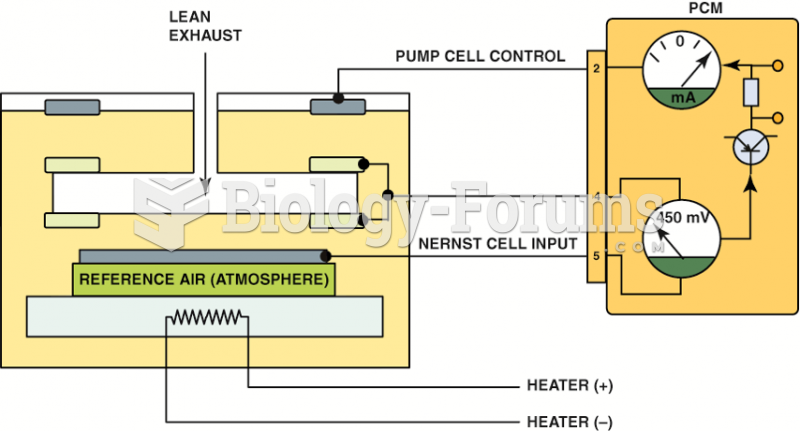
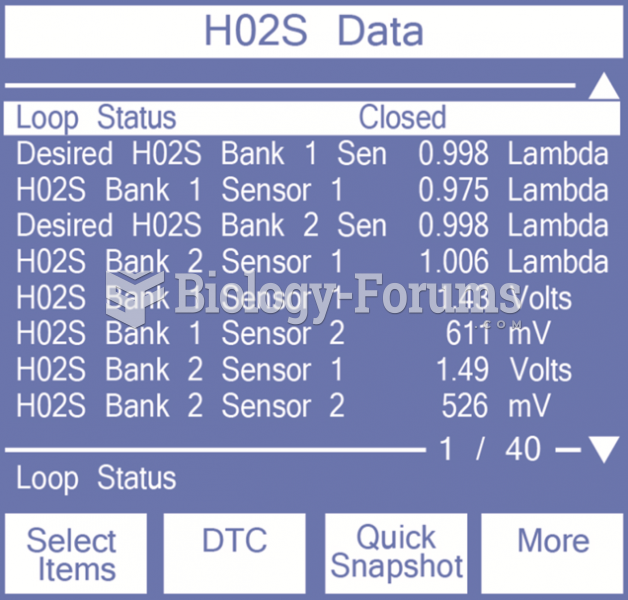
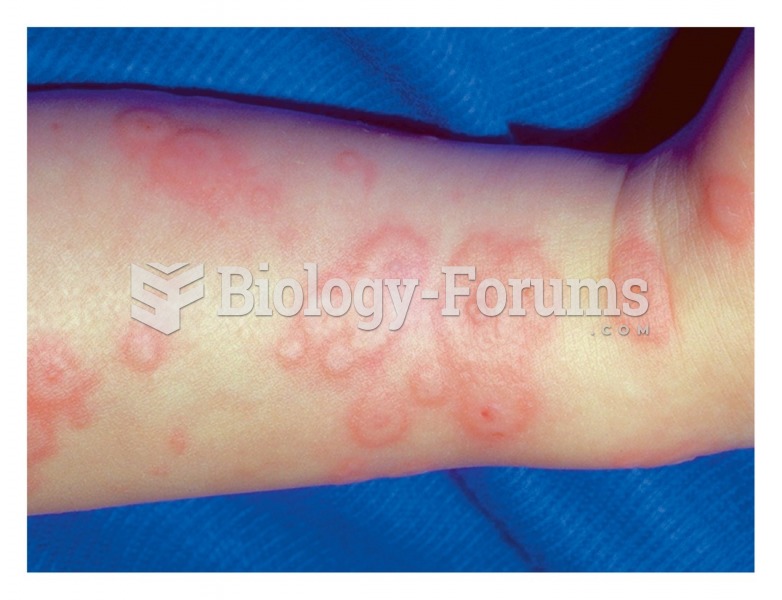
|
|
|
The effects of organophosphate poisoning are referred to by using the abbreviations “SLUD” or “SLUDGE,” It stands for: salivation, lacrimation, urination, defecation, GI upset, and emesis.
The first war in which wide-scale use of anesthetics occurred was the Civil War, and 80% of all wounds were in the extremities.
Medications that are definitely not safe to take when breastfeeding include radioactive drugs, antimetabolites, some cancer (chemotherapy) agents, bromocriptine, ergotamine, methotrexate, and cyclosporine.
In the United States, there is a birth every 8 seconds, according to the U.S. Census Bureau's Population Clock.
There can actually be a 25-hour time difference between certain locations in the world. The International Date Line passes between the islands of Samoa and American Samoa. It is not a straight line, but "zig-zags" around various island chains. Therefore, Samoa and nearby islands have one date, while American Samoa and nearby islands are one day behind. Daylight saving time is used in some islands, but not in others—further shifting the hours out of sync with natural time.
 The recent mass upheavals in Tunisia, Egypt, Libya, Yemen, and Syria gave political scientists a cha
The recent mass upheavals in Tunisia, Egypt, Libya, Yemen, and Syria gave political scientists a cha
 In 2008, the U.S. economy suffered a gaping wound as several trillion dollars were ripped out of it.
In 2008, the U.S. economy suffered a gaping wound as several trillion dollars were ripped out of it.