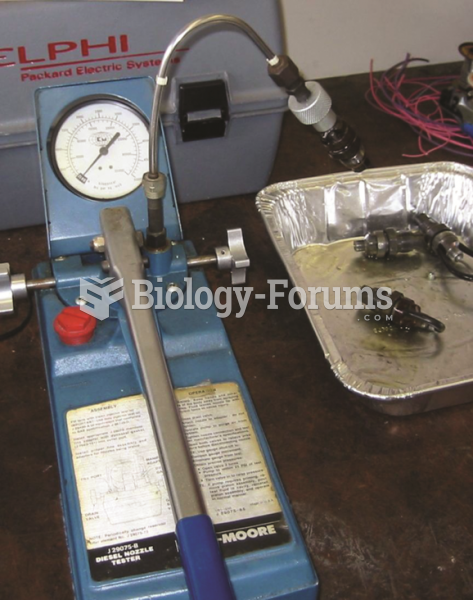
Answer to Question 1
Although the two-variable NEDV design is quite weak, you can make it considerably stronger by adding multiple outcome variables in what is known as a pattern-matching design. In this variation, you need many outcome variables and a theory that tells how affected (from most to least) by the program each variable will be. Then you collect data that allow you to assess whether the observed pattern of data matches the theoretically predicted pattern. Let's reconsider the example from the algebra program in the previous discussion. Now, instead of having only an algebra and geometry score, imagine you have ten measures that you collect pre and post. You would expect the algebra measure to be most affected by the program (because that's what the program was most designed to affect). However, in this variation, you recognize that geometry might also be somewhat affected because training in algebra might be relevant, at least to some degree, to geometry skills. On the other hand, you might theorize that creativity would be much less affected, even indirectly, by training in algebra, and so you predict the creativity measure to be the least affected of the ten measures.
Depending on the circumstances, the pattern-matching NEDV design can be quite strong with respect to internal validity. In general, the design is stronger if you have a larger set of variables and your expectation pattern matches well with the observed results. What are the threats to internal validity in this design? Only a factor (such as an historical event or a maturational pattern) that would yield the same ordered outcome pattern can act as an alternative explanation. Furthermore, the more complex the predicted pattern, the less likely it is that some other factor would yield it. The problem is, the more complex the predicted pattern, the less likely it is that you will find it matches your observed data as well.
The pattern-matching notion implicit in the NEDV design requires an entirely different approach to causal assessment, one that depends on detailed prior explication of the program and its expected effects. It suggests a much richer model for causal assessment than one that relies only on a simplistic dichotomous treatment-control model.
Answer to Question 2
F