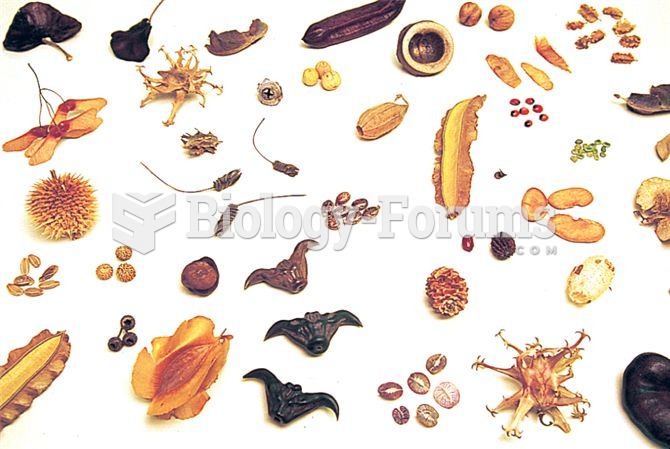
Answer to Question 1
d
Answer to Question 2
In snowball sampling, you begin by identifying people who meet the criteria for inclusion in your study. You then ask them to recommend others they know who also meet the criteria. Although this method would hardly lead to representative samples, at times it may be the best method available. Snowball sampling is especially useful when you are trying to reach populations that are inaccessible or hard to find. For instance, if you are studying the homeless, you are not likely to be able to find good lists of homeless people within a specific geographical area. However, if you go to that area and identify one or two, you may find that they know who the other homeless people in their vicinity are and how you can find them.
The advantage of snowball sampling is that it can achieve broad coverage of a population, because respondents, including those who do not attend public venues, are reached through their social networks. However, the biggest disadvantage of this method is that because respondents are not randomly selected, and are dependent on the subjective choices of the first respondents, snowball samples are more likely to be biased.
A recent development in sampling methodology, respondent-driven sampling (RDS), was designed to overcome some of these limitations by providing breadth of coverage with statistical validity. RDS combines a modified form of chain-referral, or snowball, sampling, with a mathematical system for weighting the sample to compensate for its not having been drawn as a simple random sample. The method is based on mathematical modeling that is possible when certain information about the respondents and their social network can be collected. The development of RDS means that hard-to-reach populations (e.g., homeless drug users) can now be studied with confidence that approaches that of probabilistic methods, a development that has the potential to revolutionize sampling and have a large impact on social science.