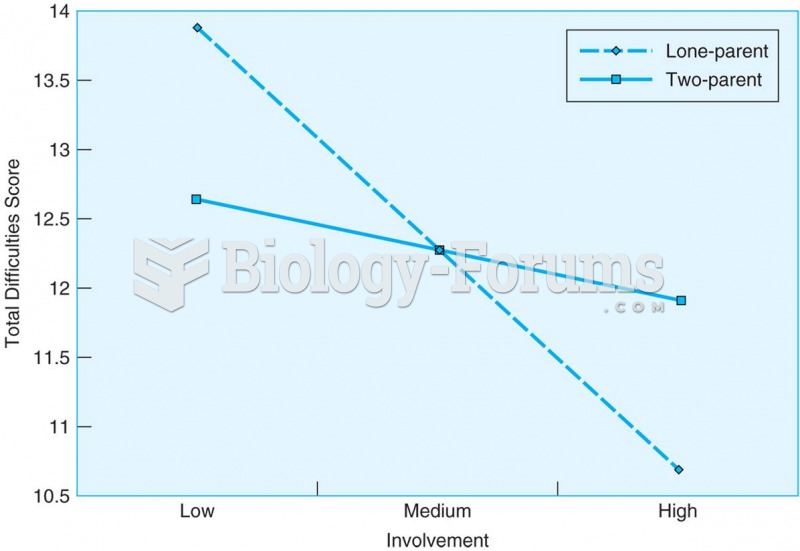
|
|
|
The cure for trichomoniasis is easy as long as the patient does not drink alcoholic beverages for 24 hours. Just a single dose of medication is needed to rid the body of the disease. However, without proper precautions, an individual may contract the disease repeatedly. In fact, most people develop trichomoniasis again within three months of their last treatment.
The most dangerous mercury compound, dimethyl mercury, is so toxic that even a few microliters spilled on the skin can cause death. Mercury has been shown to accumulate in higher amounts in the following types of fish than other types: swordfish, shark, mackerel, tilefish, crab, and tuna.
In most cases, kidneys can recover from almost complete loss of function, such as in acute kidney (renal) failure.
To combat osteoporosis, changes in lifestyle and diet are recommended. At-risk patients should include 1,200 to 1,500 mg of calcium daily either via dietary means or with supplements.
Many of the drugs used by neuroscientists are derived from toxic plants and venomous animals (such as snakes, spiders, snails, and puffer fish).
 An additional extension may be necessary to hoist a truck or van equipped with running boards to ...
An additional extension may be necessary to hoist a truck or van equipped with running boards to ...
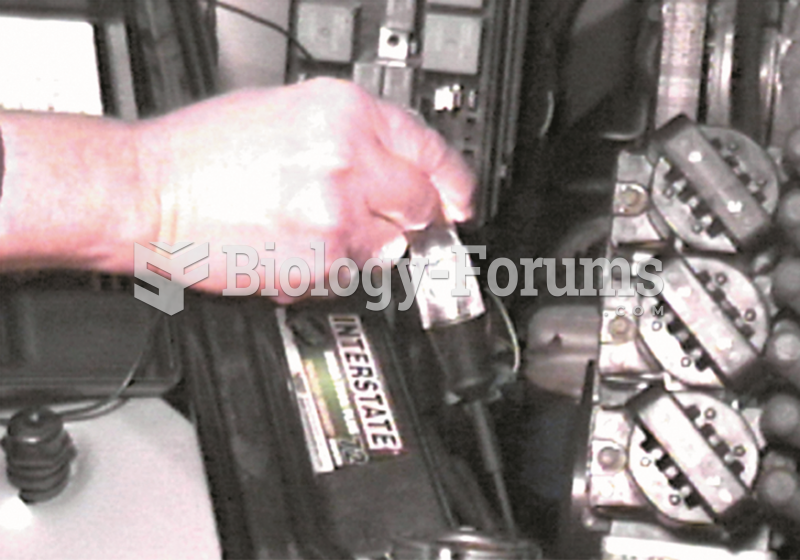 Touch the test light to the negative (–) terminal of the battery or a good engine ground to check ...
Touch the test light to the negative (–) terminal of the battery or a good engine ground to check ...