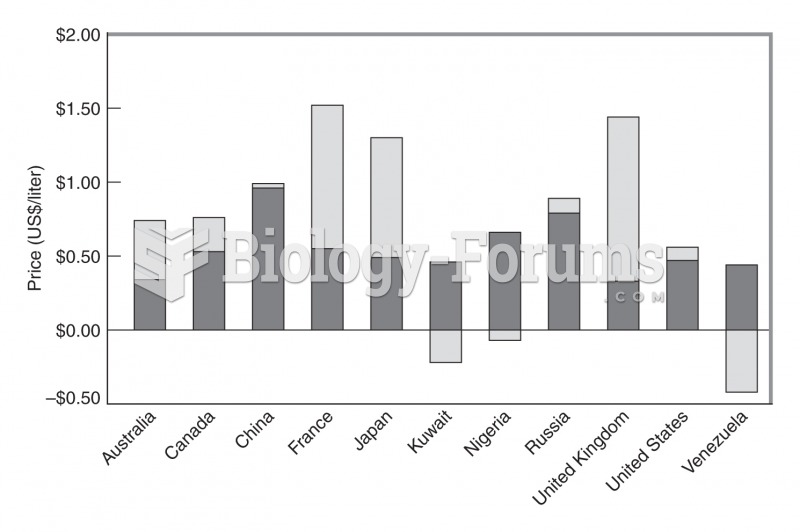
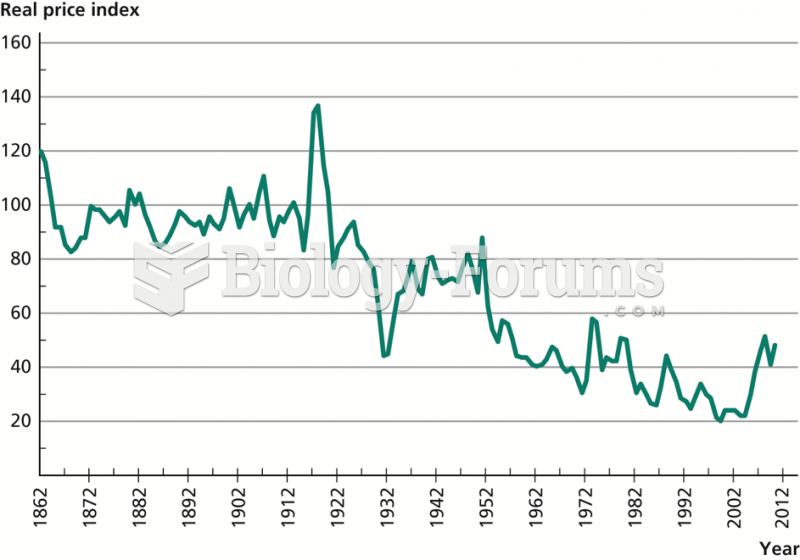
|
|
|
Since 1988, the CDC has reported a 99% reduction in bacterial meningitis caused by Haemophilus influenzae, due to the introduction of the vaccine against it.
Approximately one in four people diagnosed with diabetes will develop foot problems. Of these, about one-third will require lower extremity amputation.
Over time, chronic hepatitis B virus and hepatitis C virus infections can progress to advanced liver disease, liver failure, and hepatocellular carcinoma. Unlike other forms, more than 80% of hepatitis C infections become chronic and lead to liver disease. When combined with hepatitis B, hepatitis C now accounts for 75% percent of all cases of liver disease around the world. Liver failure caused by hepatitis C is now leading cause of liver transplants in the United States.
More than 30% of American adults, and about 12% of children utilize health care approaches that were developed outside of conventional medicine.
Asthma-like symptoms were first recorded about 3,500 years ago in Egypt. The first manuscript specifically written about asthma was in the year 1190, describing a condition characterized by sudden breathlessness. The treatments listed in this manuscript include chicken soup, herbs, and sexual abstinence.
 As China has embraced its version of capitalism, wealth has grown, as has consumption. Luxury goods ...
As China has embraced its version of capitalism, wealth has grown, as has consumption. Luxury goods ...
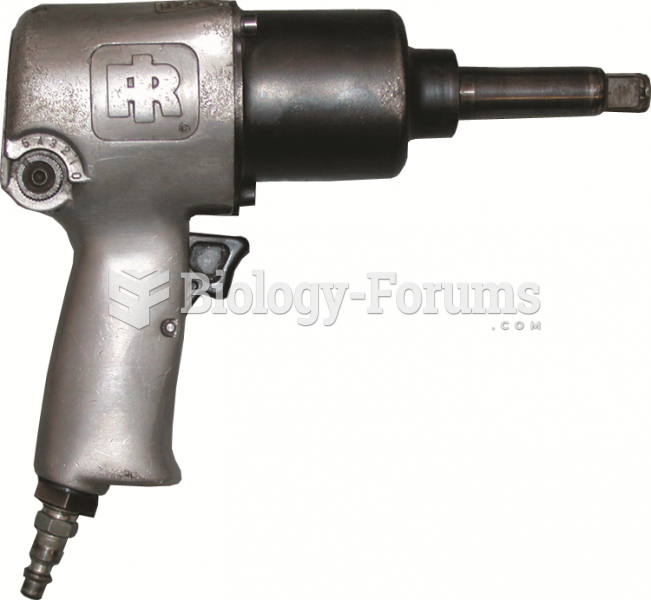 A typical 1/2 inch drive air impact wrench. The direction of rotation can be changed to loosen or ...
A typical 1/2 inch drive air impact wrench. The direction of rotation can be changed to loosen or ...