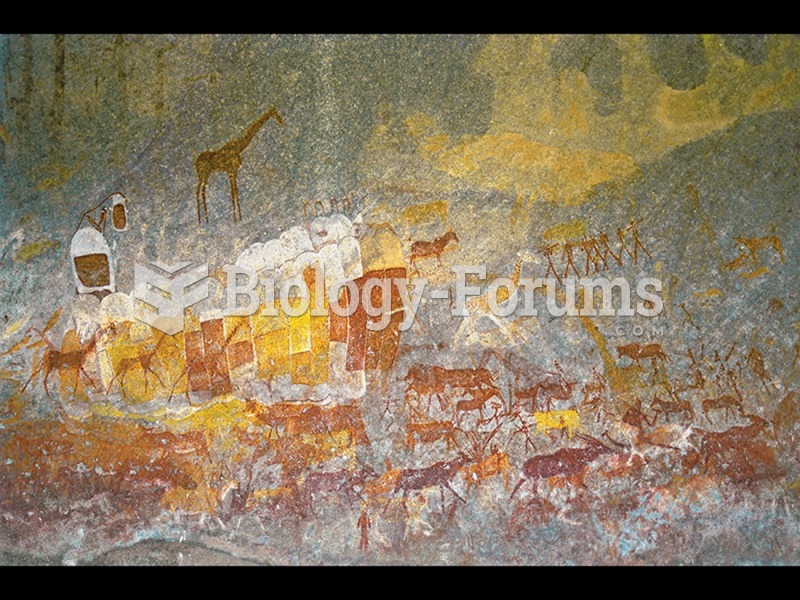
|
|
|
Multiple experimental evidences have confirmed that at the molecular level, cancer is caused by lesions in cellular DNA.
Most strokes are caused when blood clots move to a blood vessel in the brain and block blood flow to that area. Thrombolytic therapy can be used to dissolve the clot quickly. If given within 3 hours of the first stroke symptoms, this therapy can help limit stroke damage and disability.
Fungal nail infections account for up to 30% of all skin infections. They affect 5% of the general population—mostly people over the age of 70.
For about 100 years, scientists thought that peptic ulcers were caused by stress, spicy food, and alcohol. Later, researchers added stomach acid to the list of causes and began treating ulcers with antacids. Now it is known that peptic ulcers are predominantly caused by Helicobacter pylori, a spiral-shaped bacterium that normally exist in the stomach.
Your chance of developing a kidney stone is 1 in 10. In recent years, approximately 3.7 million people in the United States were diagnosed with a kidney disease.