|
|
|
Hyperthyroidism leads to an increased rate of metabolism and affects about 1% of women but only 0.1% of men. For most people, this increased metabolic rate causes the thyroid gland to become enlarged (known as a goiter).
The first monoclonal antibodies were made exclusively from mouse cells. Some are now fully human, which means they are likely to be safer and may be more effective than older monoclonal antibodies.
The first oncogene was discovered in 1970 and was termed SRC (pronounced "SARK").
Illness; diuretics; laxative abuse; hot weather; exercise; sweating; caffeine; alcoholic beverages; starvation diets; inadequate carbohydrate consumption; and diets high in protein, salt, or fiber can cause people to become dehydrated.
The U.S. Pharmacopeia Medication Errors Reporting Program states that approximately 50% of all medication errors involve insulin.
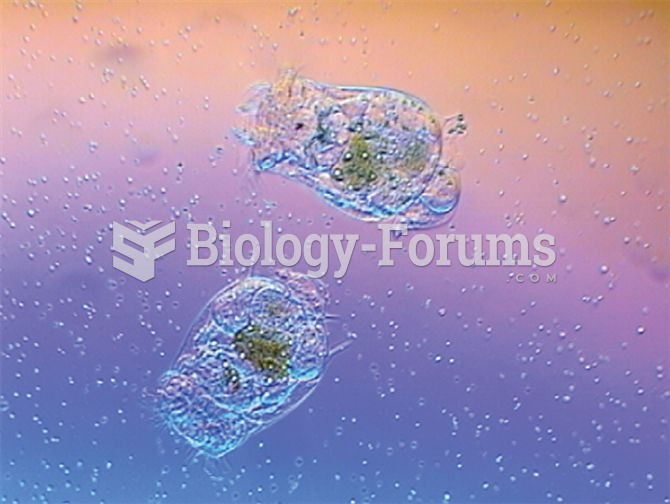 The rotifer, Brachionus calyciflorus, is a large predator that consumes the smaller algae, Chlorella
The rotifer, Brachionus calyciflorus, is a large predator that consumes the smaller algae, Chlorella
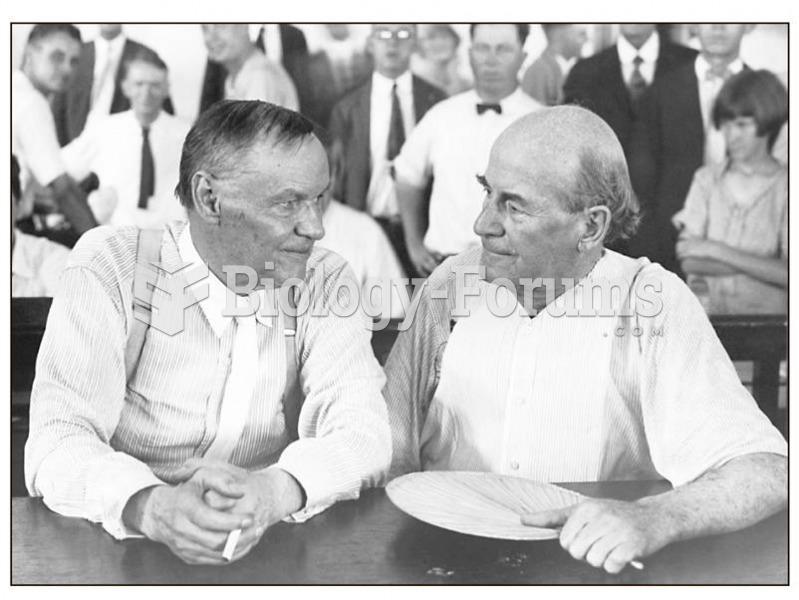 The Scopes Trial: William Jennings Bryan (right) represented the state of Tennessee, and Clarence Da
The Scopes Trial: William Jennings Bryan (right) represented the state of Tennessee, and Clarence Da