|
|
|
Although puberty usually occurs in the early teenage years, the world's youngest parents were two Chinese children who had their first baby when they were 8 and 9 years of age.
Allergies play a major part in the health of children. The most prevalent childhood allergies are milk, egg, soy, wheat, peanuts, tree nuts, and seafood.
Hypertension is a silent killer because it is deadly and has no significant early symptoms. The danger from hypertension is the extra load on the heart, which can lead to hypertensive heart disease and kidney damage. This occurs without any major symptoms until the high blood pressure becomes extreme. Regular blood pressure checks are an important method of catching hypertension before it can kill you.
Your heart beats over 36 million times a year.
Ether was used widely for surgeries but became less popular because of its flammability and its tendency to cause vomiting. In England, it was quickly replaced by chloroform, but this agent caused many deaths and lost popularity.
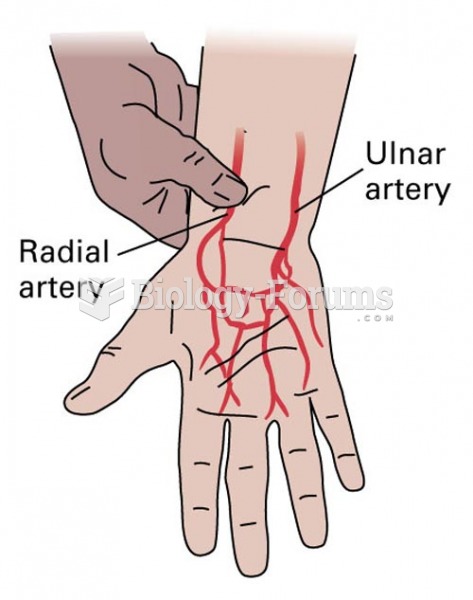 Allen Test: A patent ulnar artery reveals the return of palm perfusion despite radial artery compres
Allen Test: A patent ulnar artery reveals the return of palm perfusion despite radial artery compres
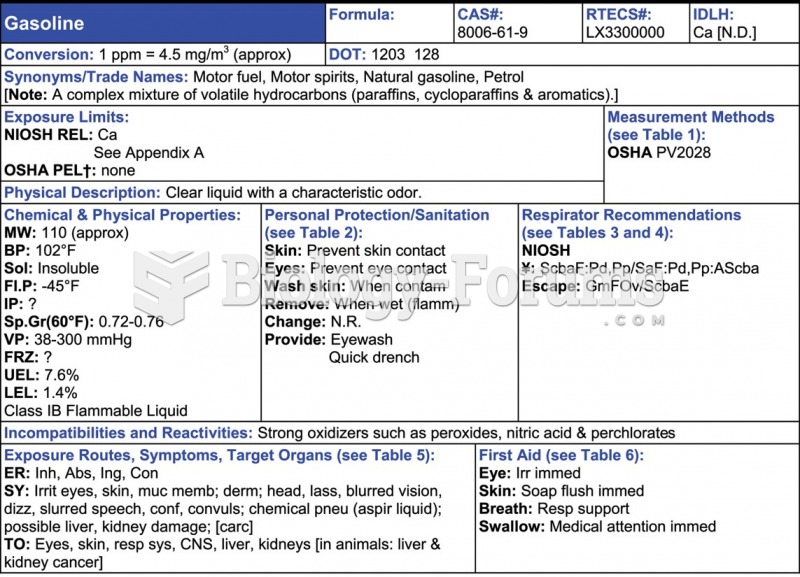
 MSDS labels provide an abridged version of substance hazards information and must be permanently ...
MSDS labels provide an abridged version of substance hazards information and must be permanently ...
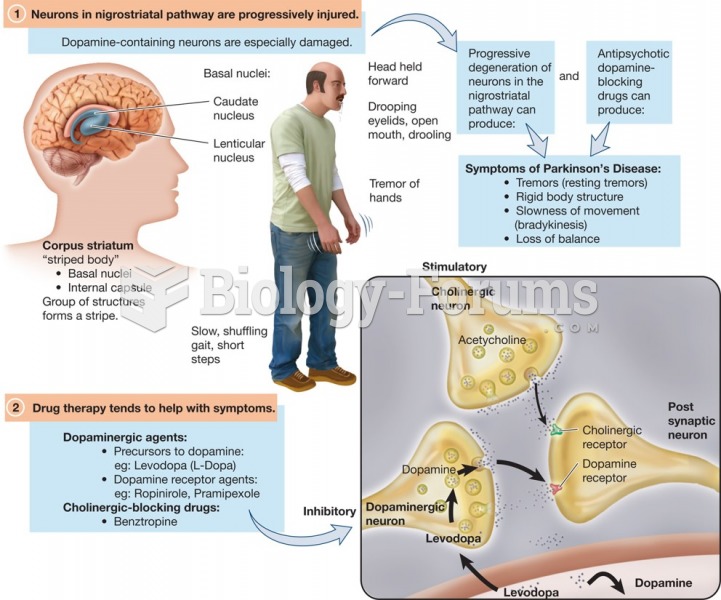 Dopamine cannot cross the blood–brain barrier. Levodopa, its precursor, can. Once levodopa crosses ...
Dopamine cannot cross the blood–brain barrier. Levodopa, its precursor, can. Once levodopa crosses ...