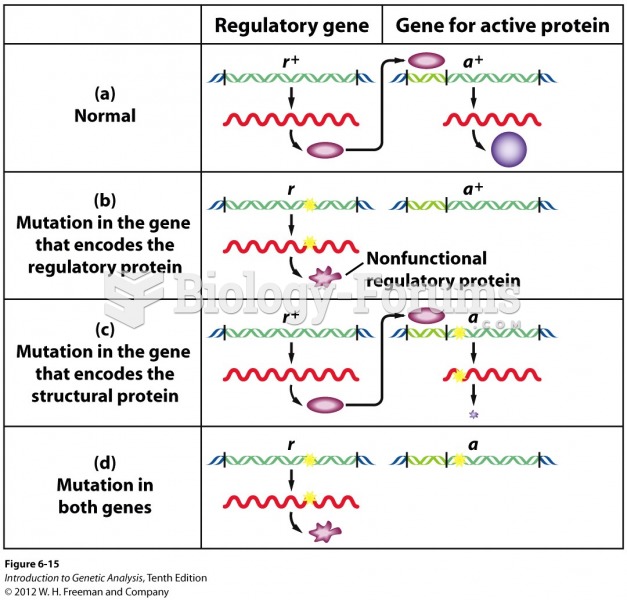
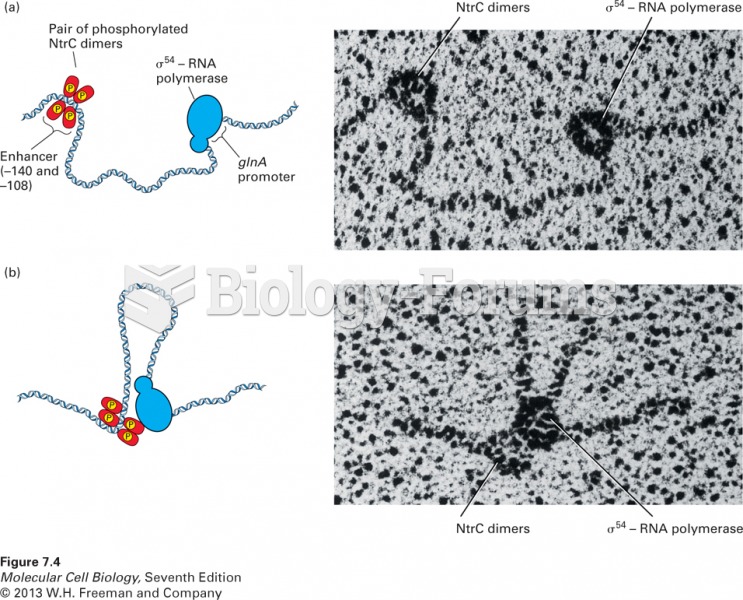
|
|
|
The heart is located in the center of the chest, with part of it tipped slightly so that it taps against the left side of the chest.
Bacteria have flourished on the earth for over three billion years. They were the first life forms on the planet.
The familiar sounds of your heart are made by the heart's valves as they open and close.
In 1886, William Bates reported on the discovery of a substance produced by the adrenal gland that turned out to be epinephrine (adrenaline). In 1904, this drug was first artificially synthesized by Friedrich Stolz.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has released reports detailing the deaths of infants (younger than 1 year of age) who died after being given cold and cough medications. This underscores the importance of educating parents that children younger than 2 years of age should never be given over-the-counter cold and cough medications without consulting their physicians.