|
|
|
Though methadone is often used to treat dependency on other opioids, the drug itself can be abused. Crushing or snorting methadone can achieve the opiate "rush" desired by addicts. Improper use such as these can lead to a dangerous dependency on methadone. This drug now accounts for nearly one-third of opioid-related deaths.
Approximately 70% of expectant mothers report experiencing some symptoms of morning sickness during the first trimester of pregnancy.
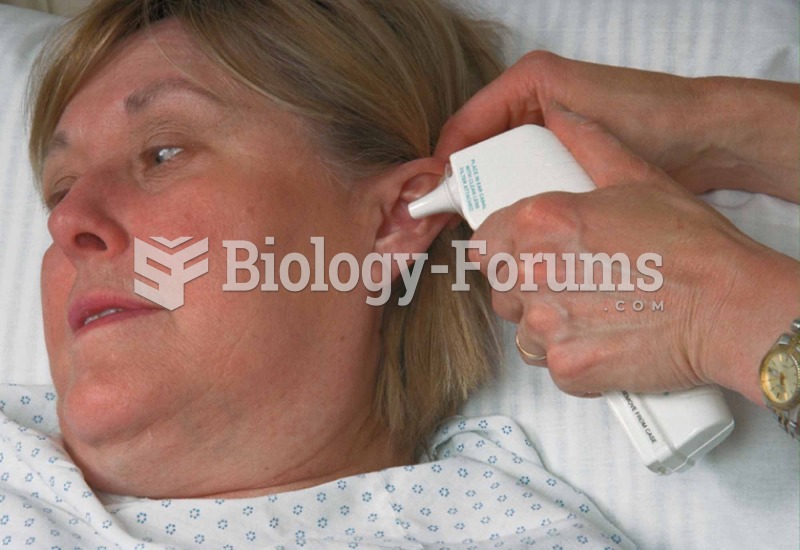
A headache when you wake up in the morning is indicative of sinusitis. Other symptoms of sinusitis can include fever, weakness, tiredness, a cough that may be more severe at night, and a runny nose or nasal congestion.
Once thought to have neurofibromatosis, Joseph Merrick (also known as "the elephant man") is now, in retrospect, thought by clinical experts to have had Proteus syndrome. This endocrine disease causes continued and abnormal growth of the bones, muscles, skin, and so on and can become completely debilitating with severe deformities occurring anywhere on the body.
Only one in 10 cancer deaths is caused by the primary tumor. The vast majority of cancer mortality is caused by cells breaking away from the main tumor and metastasizing to other parts of the body, such as the brain, bones, or liver.