|
|
|
When Gabriel Fahrenheit invented the first mercury thermometer, he called "zero degrees" the lowest temperature he was able to attain with a mixture of ice and salt. For the upper point of his scale, he used 96°, which he measured as normal human body temperature (we know it to be 98.6° today because of more accurate thermometers).
If you use artificial sweeteners, such as cyclamates, your eyes may be more sensitive to light. Other factors that will make your eyes more sensitive to light include use of antibiotics, oral contraceptives, hypertension medications, diuretics, and antidiabetic medications.
There are approximately 3 million unintended pregnancies in the United States each year.
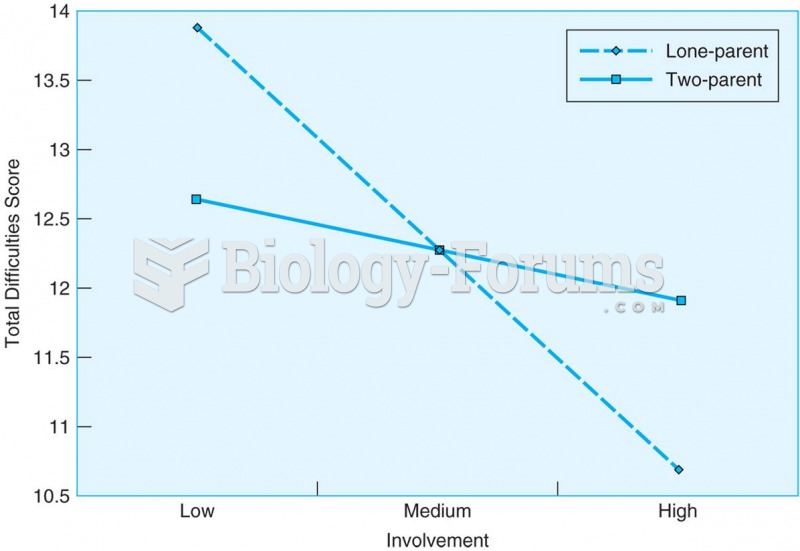
The highest suicide rate in the United States is among people ages 65 years and older. Almost 15% of people in this age group commit suicide every year.
Chronic necrotizing aspergillosis has a slowly progressive process that, unlike invasive aspergillosis, does not spread to other organ systems or the blood vessels. It most often affects middle-aged and elderly individuals, spreading to surrounding tissue in the lungs. The disease often does not respond to conventionally successful treatments, and requires individualized therapies in order to keep it from becoming life-threatening.
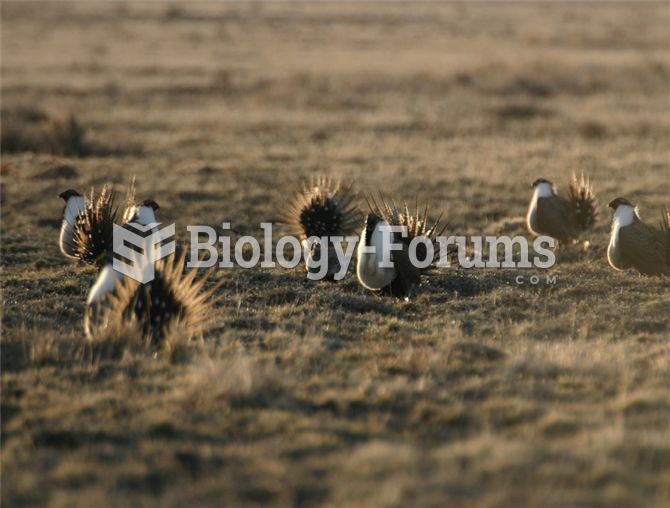 Organisms exhibit a diversity of behaviours, which include (clockwise from upper left), foraging and
Organisms exhibit a diversity of behaviours, which include (clockwise from upper left), foraging and
 Invasive species in Canada include (a) zebra mussels, Dreissena polymorpha, (b) sea lamprey, Petromy
Invasive species in Canada include (a) zebra mussels, Dreissena polymorpha, (b) sea lamprey, Petromy