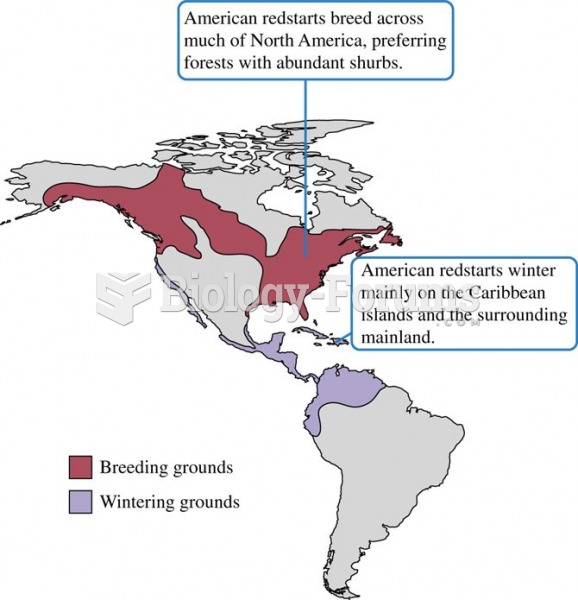
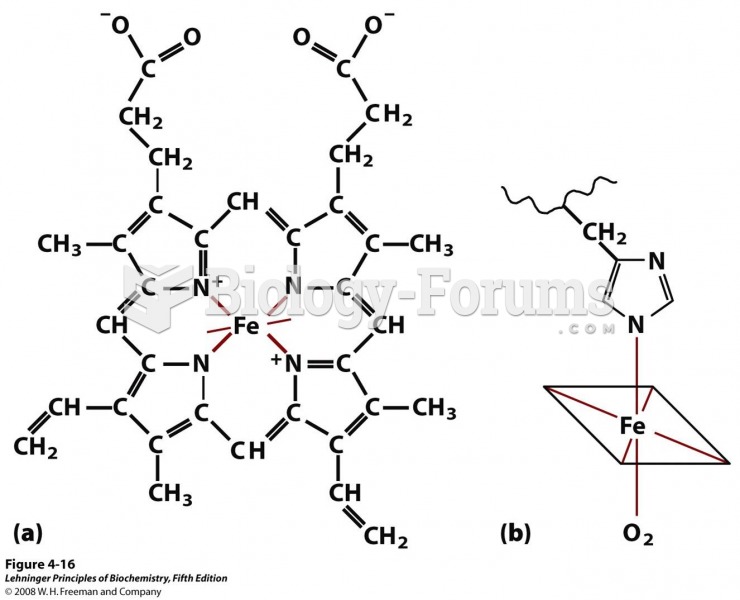
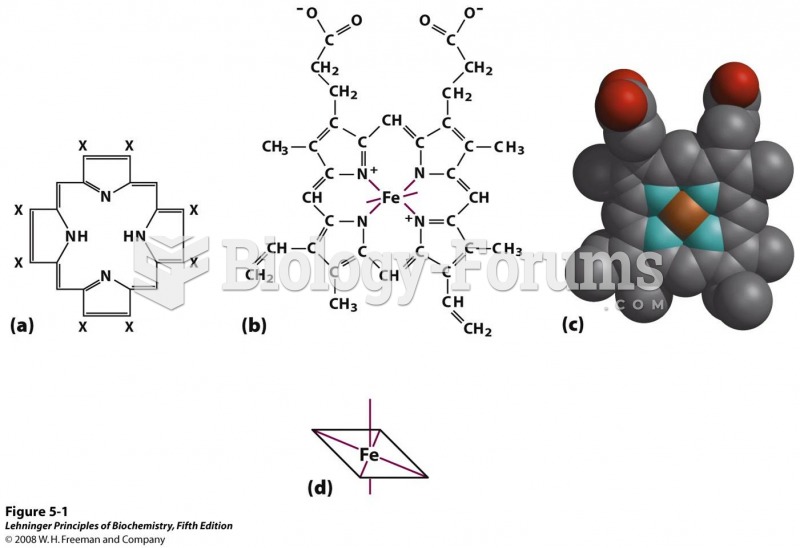
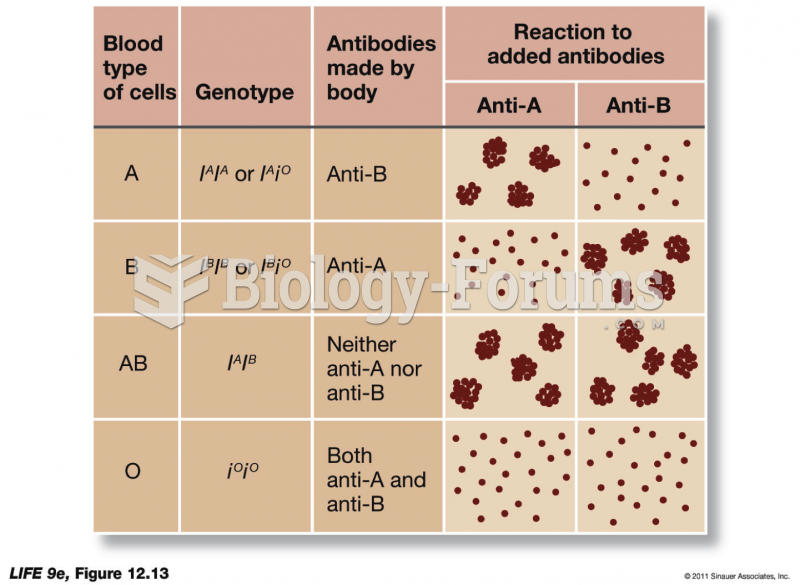
Answer to Question 1
a
Answer to Question 2
Political institutions first emerged in agrarian societies as they acquired surpluses and developed greater inequality. Elites took control of politics and used custom or traditional authority to justify their position. Monarchy is a political system in which power resides in one person or family and is passed from generation to generation through lines of inheritance. Monarchies are most common in agrarian societies and are associated with traditional authority patterns. Absolute monarchs claim a hereditary right to rule (based on membership in a noble family) or a divine right to rule (a God-given right to rule that legitimizes the exercise of power). In limited monarchies, rulers depend on powerful members of the nobility to retain their thrones. In constitutional monarchies, the royalty serve as symbolic rulers or heads of state while actual authority is held by elected officials in national parliaments (such as the United Kingdom), members of royal families primarily perform ceremonial functions. Authoritarianism is a political system controlled by rulers who deny popular participation in government. Today, Saudi Arabia and Kuwait are examples of authoritarian absolute monarchies. In dictatorships, power is gained and held by a single individual.
Pure dictatorships are rare; all rulers need the support of the military and the backing of business elites to maintain their position. Military juntas result when military officers seize power from the government. Today, authoritarian regimes exist in Cuba and in the People's Republic of China. Authoritarian regimes seek to control the media and to suppress coverage of any topics or information that does not reflect upon the regime in a favorable light. Totalitarianism is a political system in which the state seeks to regulate all aspects of people's public and private lives. Totalitarianism relies on modern technology to monitor and control people mass propaganda and electronic surveillance are widely used to influence people's thinking and control their actions. One example of a totalitarian regime was the National Socialist (Nazi) Party in Germany during World War II; military leaders there sought to control all aspects of national life. To keep people from rebelling, totalitarian governments enforce conformity; people are denied the right to assemble for political purposes, access to information is strictly controlled, and secret police enforce compliance, creating an environment of constant fear and suspicion. Democracy is a political system in which the people hold the ruling power either directly or through elected representatives. Direct participatory democracy requires that citizens be able to meet together regularly to debate and decide the issues of the day. In the United States, people have a voice in the government through representative democracy, whereby citizens elect representatives to serve as bridges between themselves and the government.