Answer to Question 1
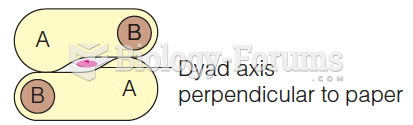
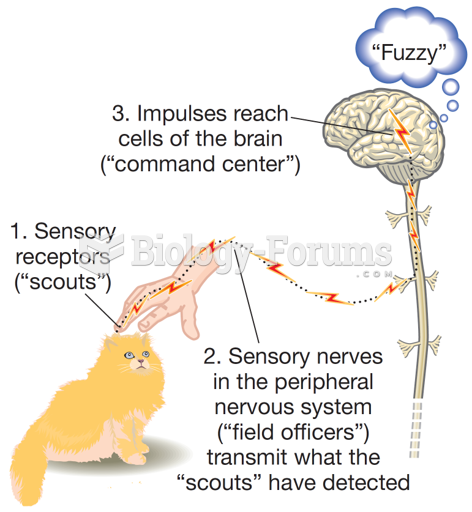
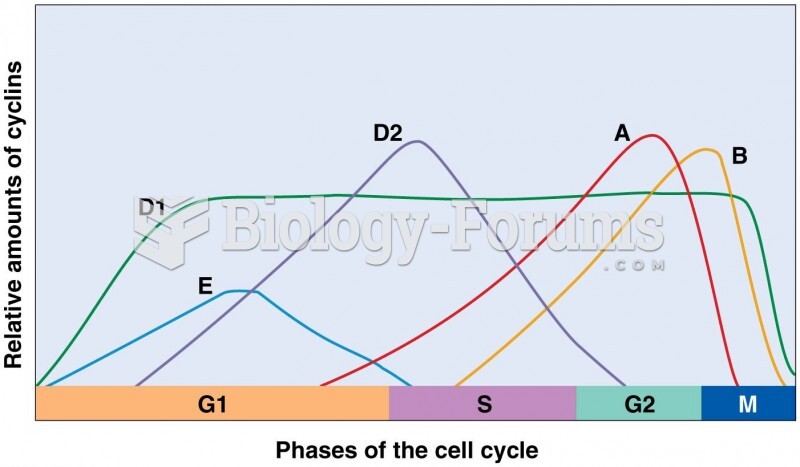
b
Answer to Question 2
Norms are established rules of behavior or standards of conduct. Norms can be classified according to their relative social importance. Folkways are informal norms or everyday customs that may be violated without serious consequences within a particular culture. They provide rules for conduct but are not considered essential to society's survival. Folkways are culture specific; they are learned patterns of behavior that can vary markedly from one society to another. For example, in the United States, folkways include using underarm deodorant, brushing our teeth, and wearing appropriate clothing for a specific occasion. Norms can also be considered to be highly essential to the stability of society. Mores are a particular culture's strongly held norms with moral and ethical connotations that may not be violated without serious consequences. Taboos are mores so strong that their violation is considered to be extremely offensive and even unmentionable. The incest taboo, which prohibits sexual or marital relations between certain categories of kin, is an example of a nearly universal taboo. Folkways and mores provide structure and security in a society. They make everyday life more predictable and provide people with some guidelines for appearance and behavior. As individuals travel in countries other than their own, they become aware of cross-cultural differences in folkways and mores.
For example, women from the United States in Muslim nations quickly become aware of mores, based on the Sharia (the edicts of the Quran) that prescribe the dominance of men over women.