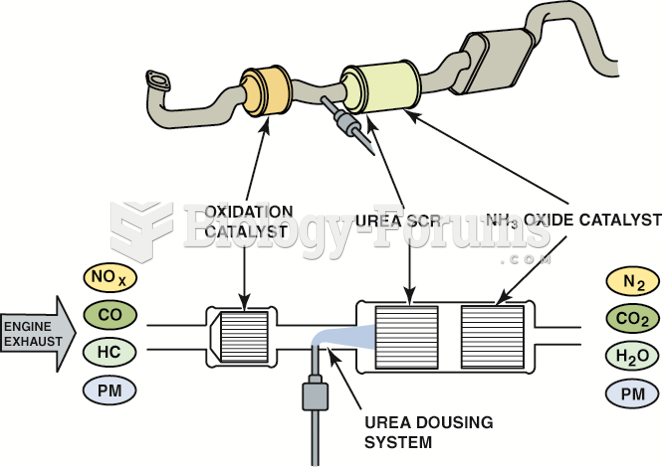
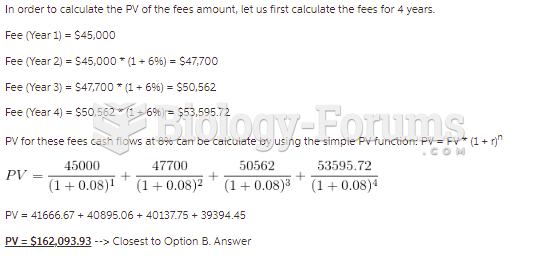
|
|
|
Acetaminophen (Tylenol) in overdose can seriously damage the liver. It should never be taken by people who use alcohol heavily; it can result in severe liver damage and even a condition requiring a liver transplant.
In the United States, there is a birth every 8 seconds, according to the U.S. Census Bureau's Population Clock.
Cytomegalovirus affects nearly the same amount of newborns every year as Down syndrome.
Anti-aging claims should not ever be believed. There is no supplement, medication, or any other substance that has been proven to slow or stop the aging process.
GI conditions that will keep you out of the U.S. armed services include ulcers, varices, fistulas, esophagitis, gastritis, congenital abnormalities, inflammatory bowel disease, enteritis, colitis, proctitis, duodenal diverticula, malabsorption syndromes, hepatitis, cirrhosis, cysts, abscesses, pancreatitis, polyps, certain hemorrhoids, splenomegaly, hernias, recent abdominal surgery, GI bypass or stomach stapling, and artificial GI openings.
 The medical assisting profession offers many settings in which to pursue your career. Good communica
The medical assisting profession offers many settings in which to pursue your career. Good communica
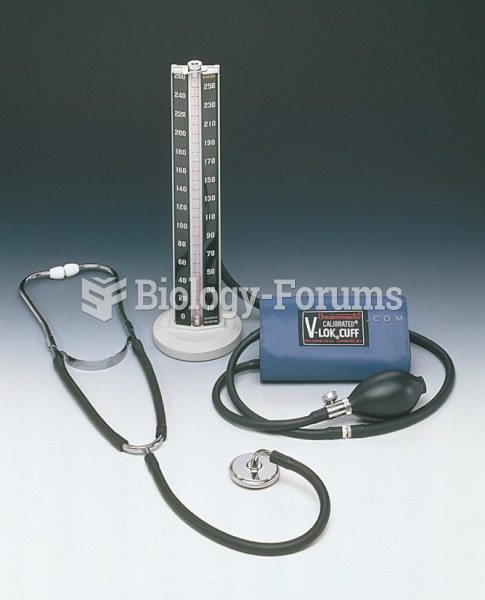 A portable mercury sphygmomanometer. Mercury versions are being phased out of medical offices and ...
A portable mercury sphygmomanometer. Mercury versions are being phased out of medical offices and ...