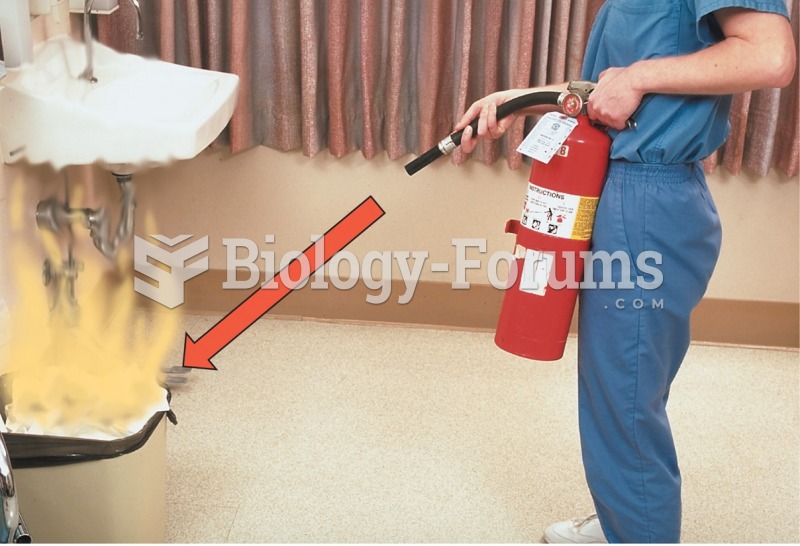
|
|
|
The cure for trichomoniasis is easy as long as the patient does not drink alcoholic beverages for 24 hours. Just a single dose of medication is needed to rid the body of the disease. However, without proper precautions, an individual may contract the disease repeatedly. In fact, most people develop trichomoniasis again within three months of their last treatment.
Drug-induced pharmacodynamic effects manifested in older adults include drug-induced renal toxicity, which can be a major factor when these adults are experiencing other kidney problems.
Certain chemicals, after ingestion, can be converted by the body into cyanide. Most of these chemicals have been removed from the market, but some old nail polish remover, solvents, and plastics manufacturing solutions can contain these substances.
As many as 28% of hospitalized patients requiring mechanical ventilators to help them breathe (for more than 48 hours) will develop ventilator-associated pneumonia. Current therapy involves intravenous antibiotics, but new antibiotics that can be inhaled (and more directly treat the infection) are being developed.
Thyroid conditions cause a higher risk of fibromyalgia and chronic fatigue syndrome.
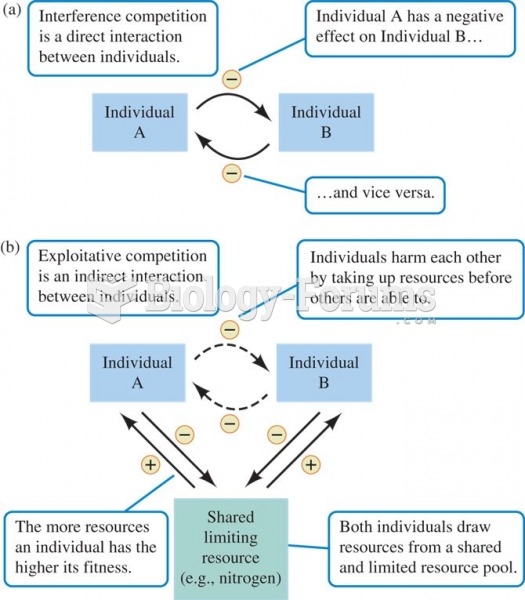 Competition can be (a) direct, or (b) indirect interaction among individuals of the same or differen
Competition can be (a) direct, or (b) indirect interaction among individuals of the same or differen
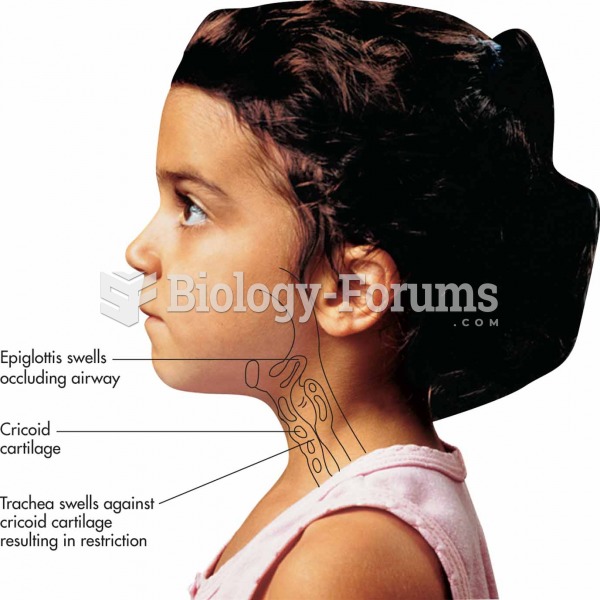 Two important changes occur in the upper airway in croup:The epiglottis swells, thereby occluding th
Two important changes occur in the upper airway in croup:The epiglottis swells, thereby occluding th