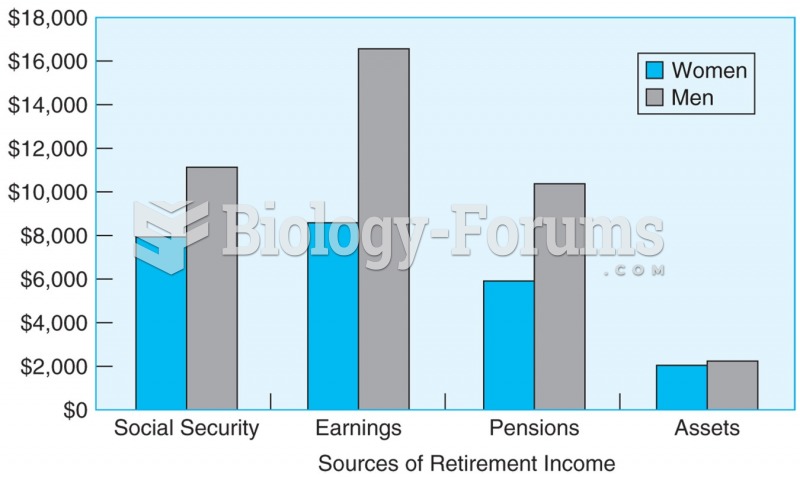
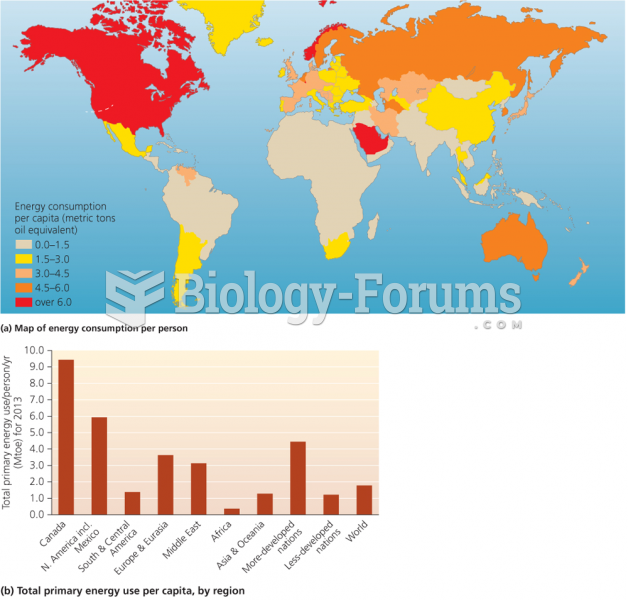
According to the symbolic interactionist perspective, why do women in poor nations bear a large number of children?
A) Men control reproductive choices in the poor nations.
B) Women cannot afford to spend money on birth control.
C) Women are not educated on how to use birth control.
D) Large families are rewarded socially and economically.
Question 2
Matching
1) demographic transition
2) population pyramid
3) fertility rate
4) fecundity
5) net migration rate
6) basic demographic equation
7) city
8) micropolis
9) human ecology
10) concentric zone model
11) sector model
12) norm of noninvolvement
13) diffusion of responsibility
14) redlining
15) enterprise zone
A) a six zone model of urban growth developed by Ernest Burgess
B) growth rate equals births minus deaths plus net migration
C) Robert Park's term for the relationship between people and their environment
D) a three-stage historical process of population growth based on birth rates and death rates
E) the use of economic incentives in a designated area to encourage investment
F) the number of children the average woman bears
G) the number of children women are capable of bearing
H) a place in which a large number of people are permanently based and do not produce their own food
I) a model of urban growth developed by Homer Hoyt that resembles wedge-shaped sections and partial circles
J) a graphic representation of a population divided into age and sex
K) a condition where people ignore their obligation to contribute to the community or group as populations or group size increase
L) the difference between the number of immigrants and emigrants per 1,000 population
M) the act of officers of a financial institution deciding not to make loans for business relocation or housing purchases in a particular area
N) a city of 10,000 to 50,000 that is not a suburb and is located next to nowhere
O) an avoidance of strangers common to residents in cities
Question 3
Matching
1) Gemeinschaft
2) Gesellschaft
3) geopolitics
4) unilinear theory
5) multilinear theory
6) dialectical process
7) invention
8) discovery
9) diffusion
10) alienation
11) distance learning
12) acid rain
13) global warming
14) environmental sociology
15) ecosabotage
A) theories that assume all societies follow the same path of development from the simple to the more complex
B) Marx's term for workers' lack of connection to the product of their labor
C) actions taken to sabotage the efforts of people who are thought to be legally harming the environment
D) modern, large, more urbanized societies that are fast changing
E) a new way of seeing reality
F) rain containing sulfuric and nitric acids (burning fossil fuels release sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxide that become sulfuric and nitric acids when they react with moisture in the air)
G) a specialty within sociology whose focus is how humans affect the environment and how the environment affects humans
H) traditional societies that are small, rural, and slow changing
I) the belief that each thesis contains its own contradiction or antithesis that must be resolved forming a synthesis
J) theories that society can follow different routes to achieve the same stage of development
K) the spread of an invention or discovery from one area to another
L) an increase in the earth's temperature due to the greenhouse effect
M) the realignment of the world's powers since World War II
N) courses taught to students who are not physically present with their instructor
O) the combination of existing elements and materials to form new ones
Question 4
A shift in the characteristics of culture and society over time is known as___________.
A) social change
B) cultural tradition
C) technology advancements
D) social life