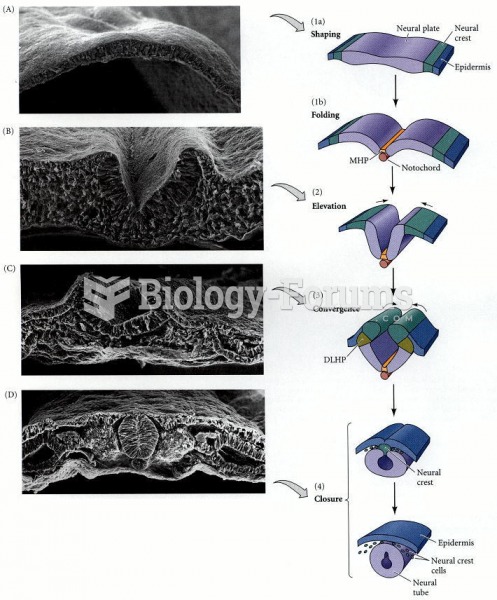
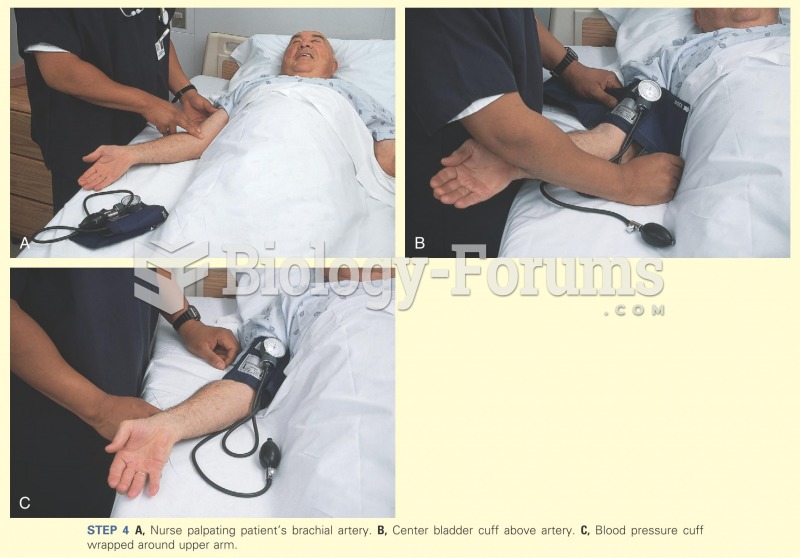
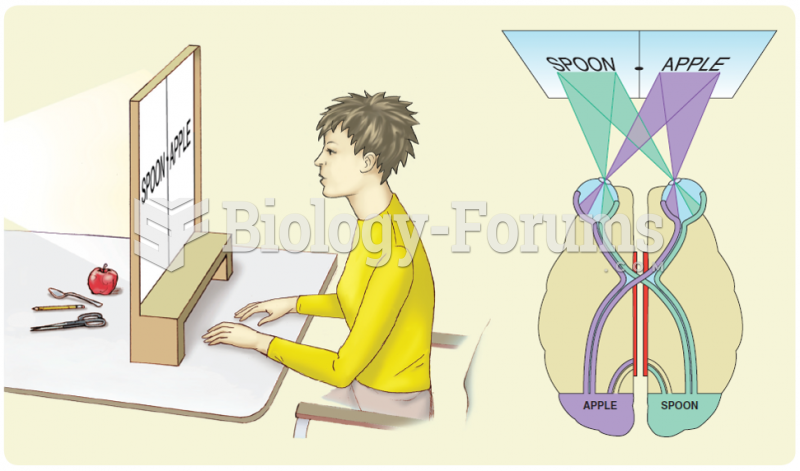
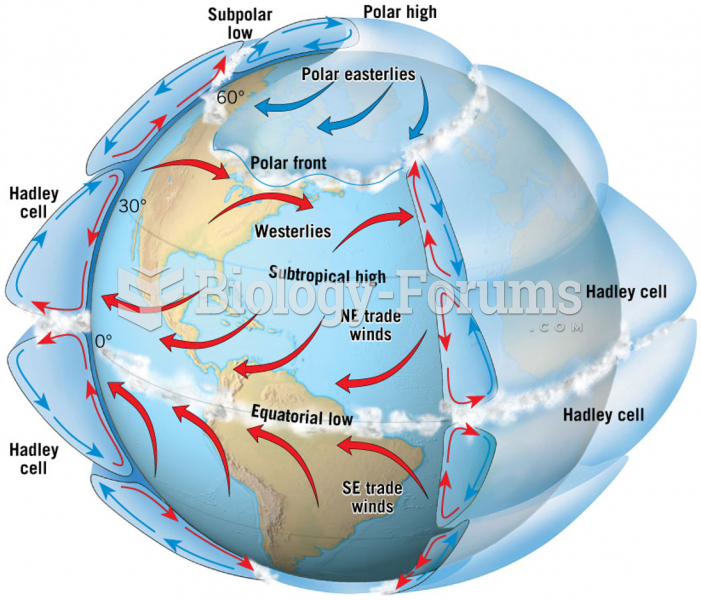
|
|
|
The National Institutes of Health have supported research into acupuncture. This has shown that acupuncture significantly reduced pain associated with osteoarthritis of the knee, when used as a complement to conventional therapies.
Adults are resistant to the bacterium that causes Botulism. These bacteria thrive in honey – therefore, honey should never be given to infants since their immune systems are not yet resistant.
Blood is approximately twice as thick as water because of the cells and other components found in it.
According to research, pregnant women tend to eat more if carrying a baby boy. Male fetuses may secrete a chemical that stimulates their mothers to step up her energy intake.
To combat osteoporosis, changes in lifestyle and diet are recommended. At-risk patients should include 1,200 to 1,500 mg of calcium daily either via dietary means or with supplements.