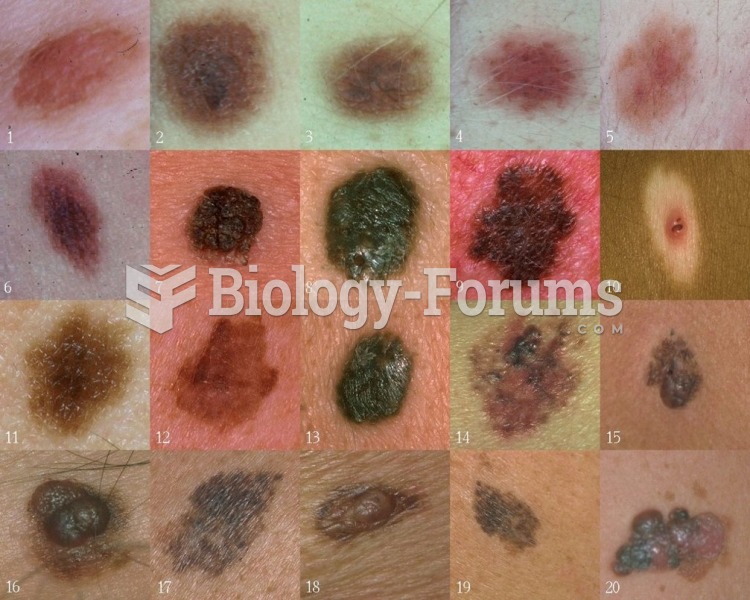
|
|
|
Looking at the sun may not only cause headache and distort your vision temporarily, but it can also cause permanent eye damage. Any exposure to sunlight adds to the cumulative effects of ultraviolet (UV) radiation on your eyes. UV exposure has been linked to eye disorders such as macular degeneration, solar retinitis, and corneal dystrophies.
Never take aspirin without food because it is likely to irritate your stomach. Never give aspirin to children under age 12. Overdoses of aspirin have the potential to cause deafness.
Anti-aging claims should not ever be believed. There is no supplement, medication, or any other substance that has been proven to slow or stop the aging process.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved Risperdal, an adult antipsychotic drug, for the symptomatic treatment of irritability in children and adolescents with autism. The approval is the first for the use of a drug to treat behaviors associated with autism in children. These behaviors are included under the general heading of irritability and include aggression, deliberate self-injury, and temper tantrums.
Fewer than 10% of babies are born on their exact due dates, 50% are born within 1 week of the due date, and 90% are born within 2 weeks of the date.