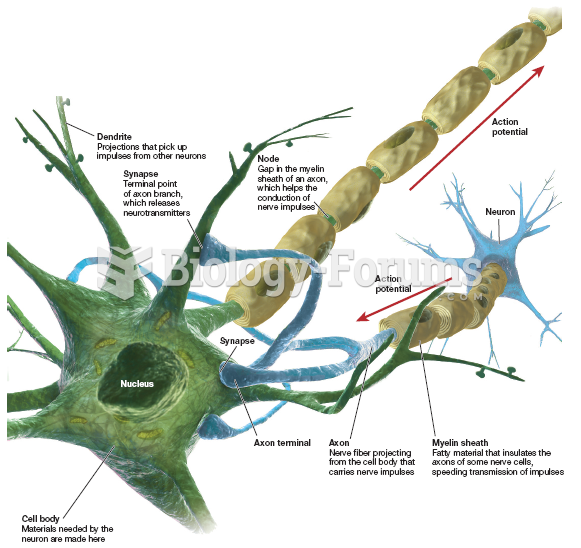
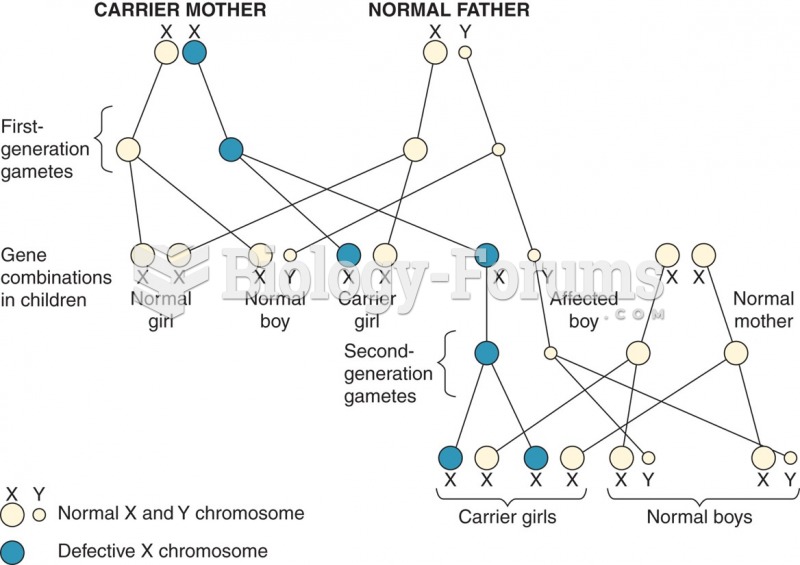
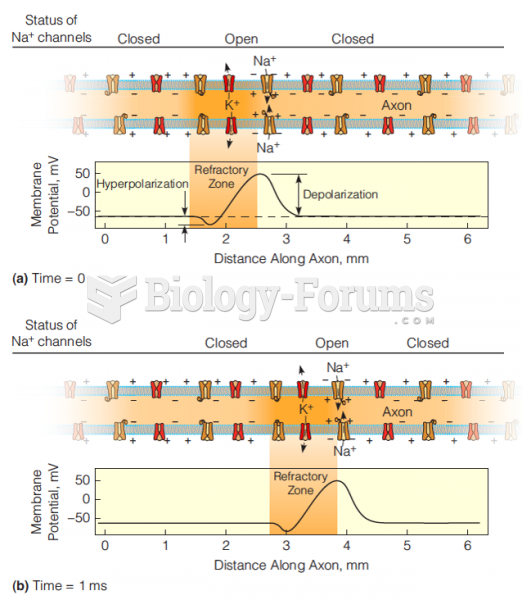
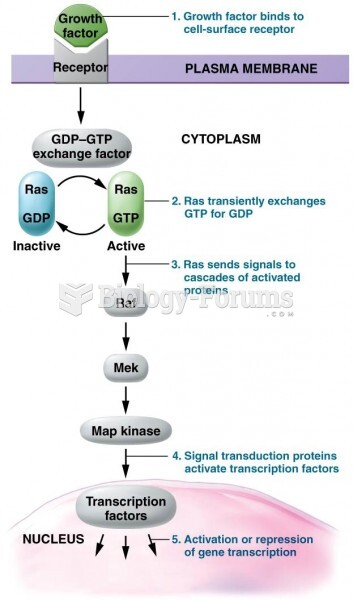
This topic contains a solution. Click here to go to the answer
|
|
|
Did you know?
Your heart beats over 36 million times a year.
Did you know?
The largest baby ever born weighed more than 23 pounds but died just 11 hours after his birth in 1879. The largest surviving baby was born in October 2009 in Sumatra, Indonesia, and weighed an astounding 19.2 pounds at birth.
Did you know?
The training of an anesthesiologist typically requires four years of college, 4 years of medical school, 1 year of internship, and 3 years of residency.
Did you know?
The average adult has about 21 square feet of skin.
Did you know?
According to the FDA, adverse drug events harmed or killed approximately 1,200,000 people in the United States in the year 2015.