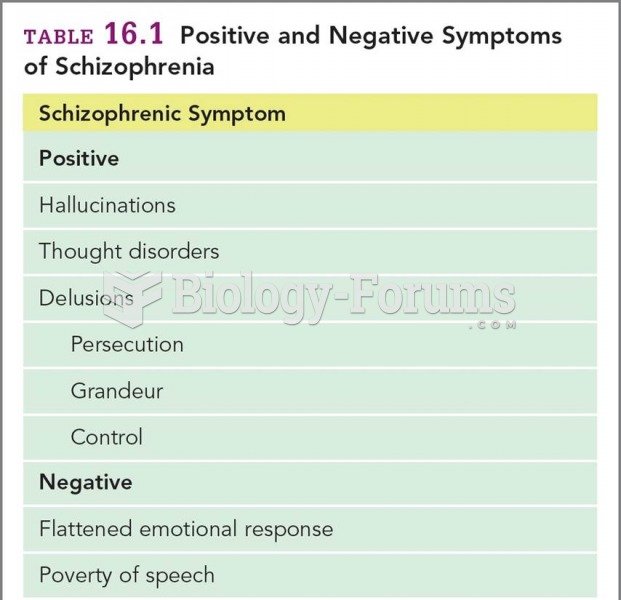
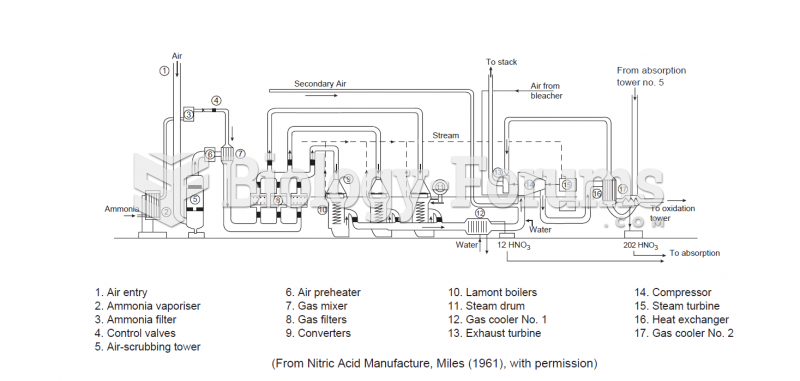
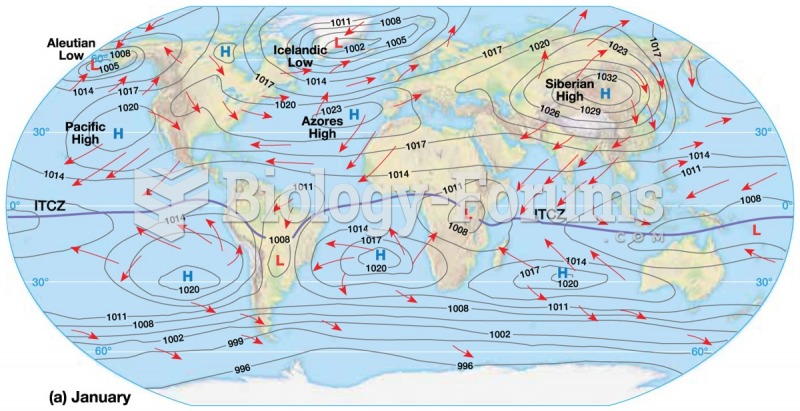
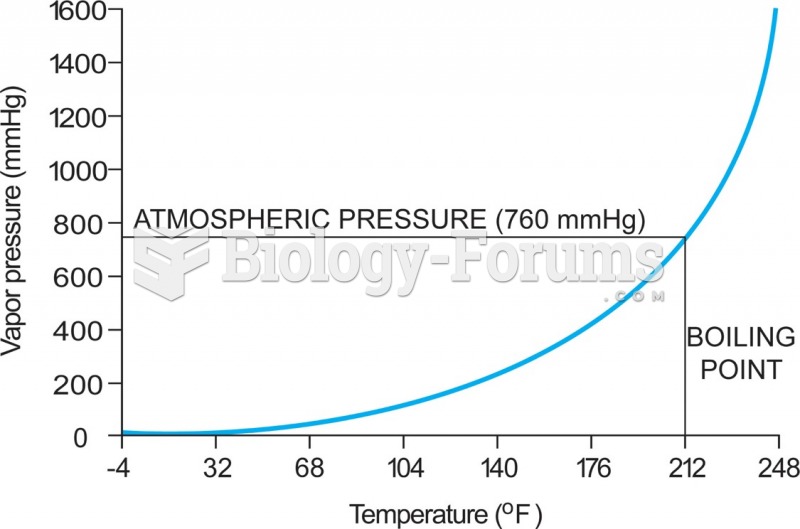
|
|
|
Many of the drugs used by neuroscientists are derived from toxic plants and venomous animals (such as snakes, spiders, snails, and puffer fish).
Pope Sylvester II tried to introduce Arabic numbers into Europe between the years 999 and 1003, but their use did not catch on for a few more centuries, and Roman numerals continued to be the primary number system.
The top 10 most important tips that will help you grow old gracefully include (1) quit smoking, (2) keep your weight down, (3) take supplements, (4) skip a meal each day or fast 1 day per week, (5) get a pet, (6) get medical help for chronic pain, (7) walk regularly, (8) reduce arguments, (9) put live plants in your living space, and (10) do some weight training.
In most climates, 8 to 10 glasses of water per day is recommended for adults. The best indicator for adequate fluid intake is frequent, clear urination.
Once thought to have neurofibromatosis, Joseph Merrick (also known as "the elephant man") is now, in retrospect, thought by clinical experts to have had Proteus syndrome. This endocrine disease causes continued and abnormal growth of the bones, muscles, skin, and so on and can become completely debilitating with severe deformities occurring anywhere on the body.