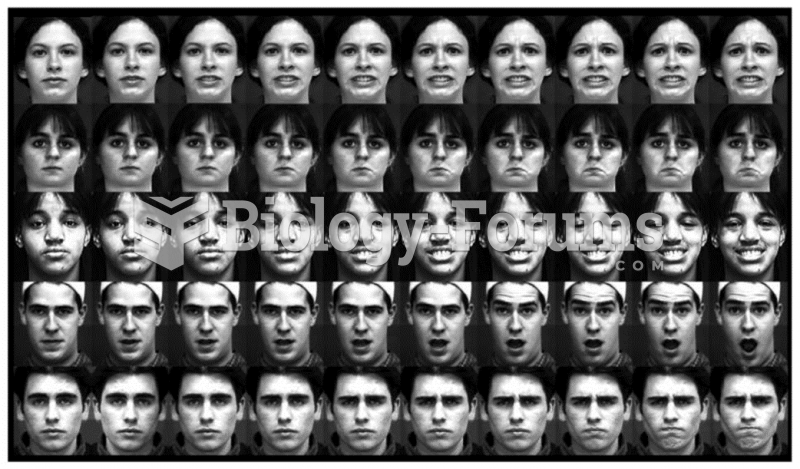
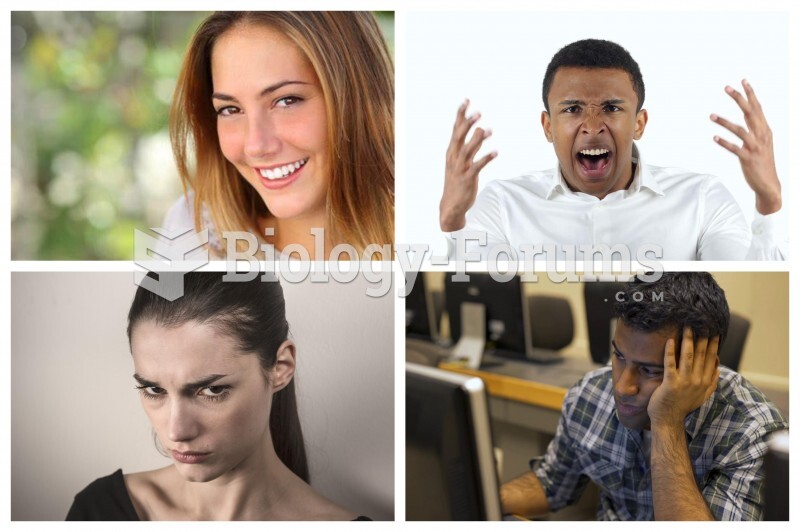
|
|
|
The most dangerous mercury compound, dimethyl mercury, is so toxic that even a few microliters spilled on the skin can cause death. Mercury has been shown to accumulate in higher amounts in the following types of fish than other types: swordfish, shark, mackerel, tilefish, crab, and tuna.
In most cases, kidneys can recover from almost complete loss of function, such as in acute kidney (renal) failure.
When blood is exposed to air, it clots. Heparin allows the blood to come in direct contact with air without clotting.
Essential fatty acids have been shown to be effective against ulcers, asthma, dental cavities, and skin disorders such as acne.
For pediatric patients, intravenous fluids are the most commonly cited products involved in medication errors that are reported to the USP.