This topic contains a solution. Click here to go to the answer
|
|
|
Did you know?
Critical care patients are twice as likely to receive the wrong medication. Of these errors, 20% are life-threatening, and 42% require additional life-sustaining treatments.
Did you know?
Alzheimer's disease affects only about 10% of people older than 65 years of age. Most forms of decreased mental function and dementia are caused by disuse (letting the mind get lazy).
Did you know?
The heart is located in the center of the chest, with part of it tipped slightly so that it taps against the left side of the chest.
Did you know?
The first oncogene was discovered in 1970 and was termed SRC (pronounced "SARK").
Did you know?
Allergies play a major part in the health of children. The most prevalent childhood allergies are milk, egg, soy, wheat, peanuts, tree nuts, and seafood.
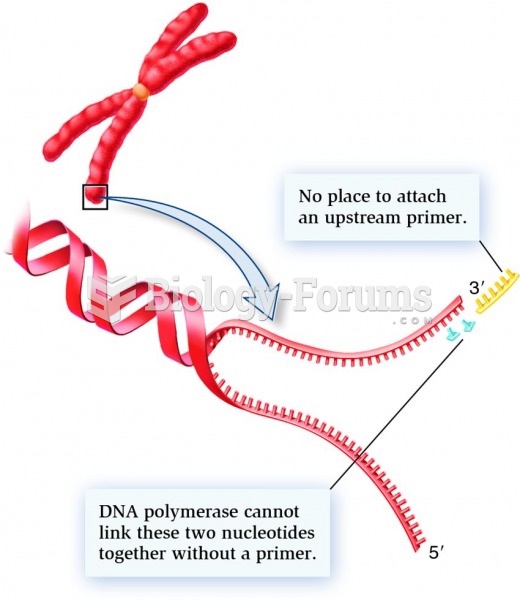 Enzymatic features of DNA polymerase that account for its inability to copy one of the DNA strands a
Enzymatic features of DNA polymerase that account for its inability to copy one of the DNA strands a
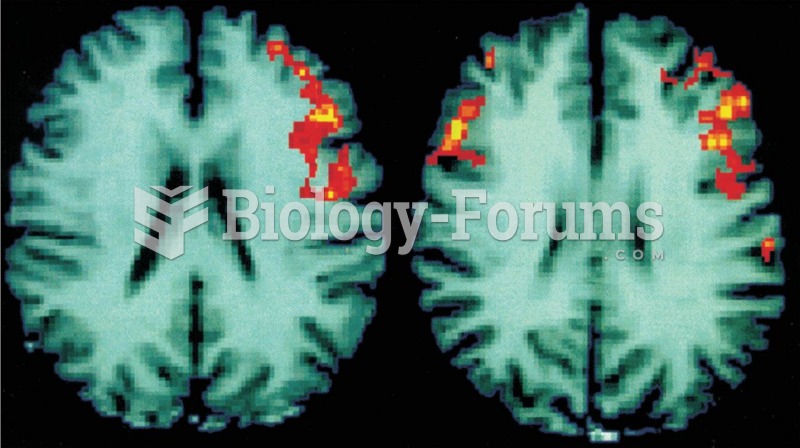 Functional MRI Scans These scans of human brains show localized average increases in neural activity
Functional MRI Scans These scans of human brains show localized average increases in neural activity