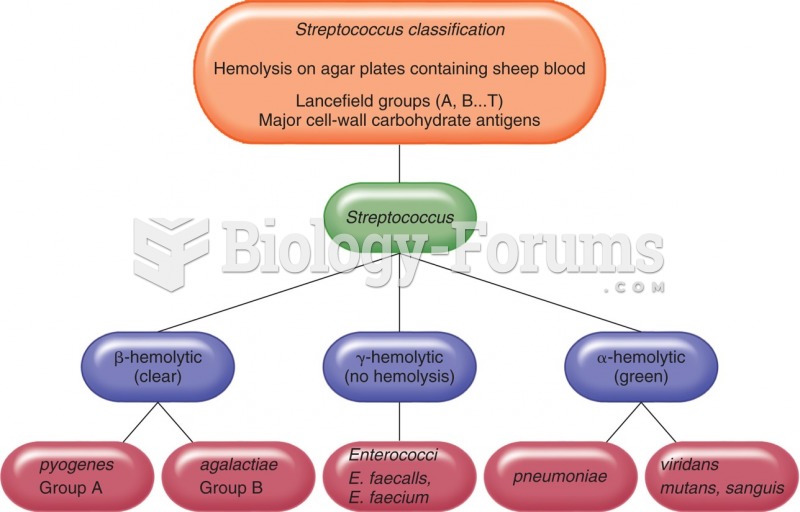
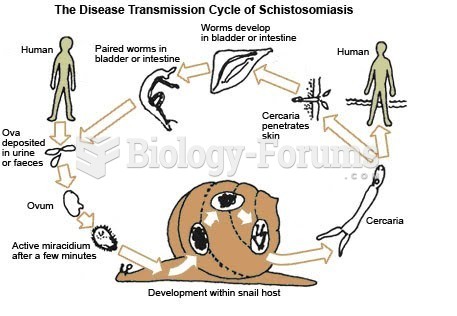
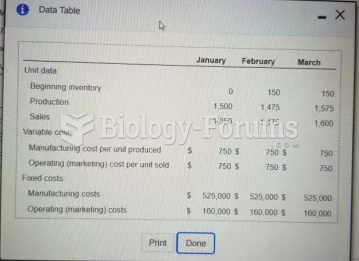
This topic contains a solution. Click here to go to the answer
|
|
|
Did you know?
Excessive alcohol use costs the country approximately $235 billion every year.
Did you know?
Your heart beats over 36 million times a year.
Did you know?
You should not take more than 1,000 mg of vitamin E per day. Doses above this amount increase the risk of bleeding problems that can lead to a stroke.
Did you know?
People about to have surgery must tell their health care providers about all supplements they take.
Did you know?
Drug-induced pharmacodynamic effects manifested in older adults include drug-induced renal toxicity, which can be a major factor when these adults are experiencing other kidney problems.