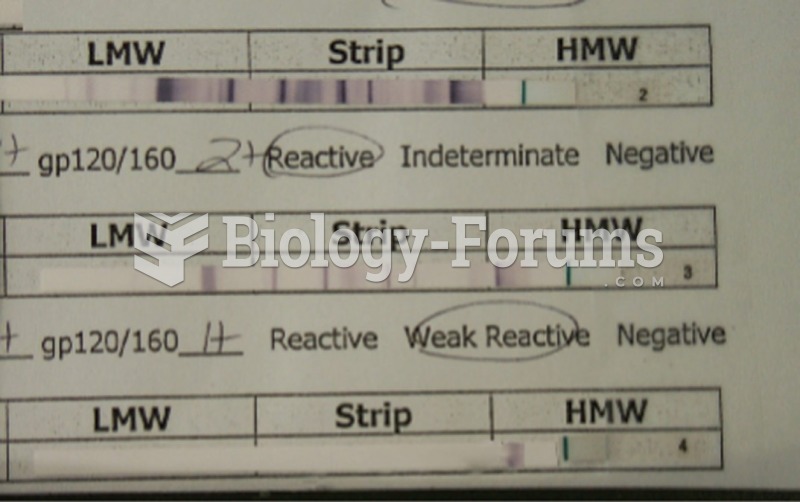
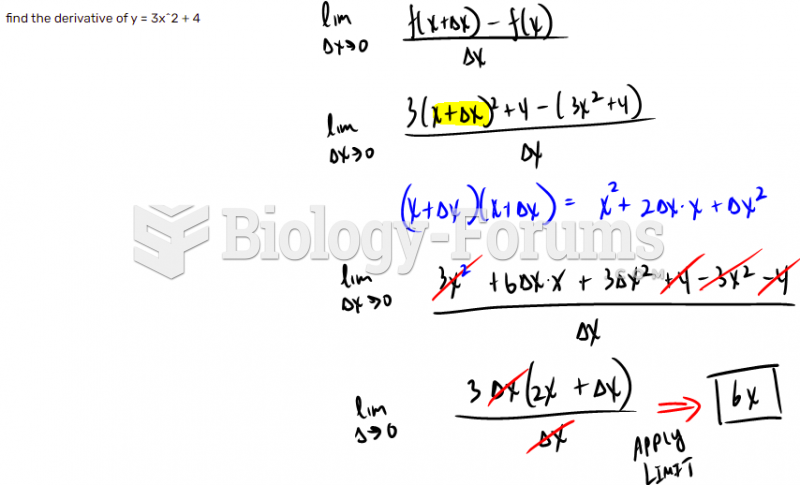
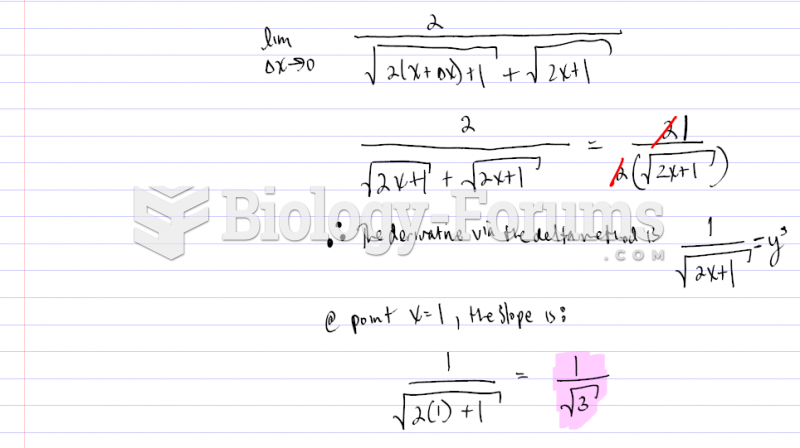
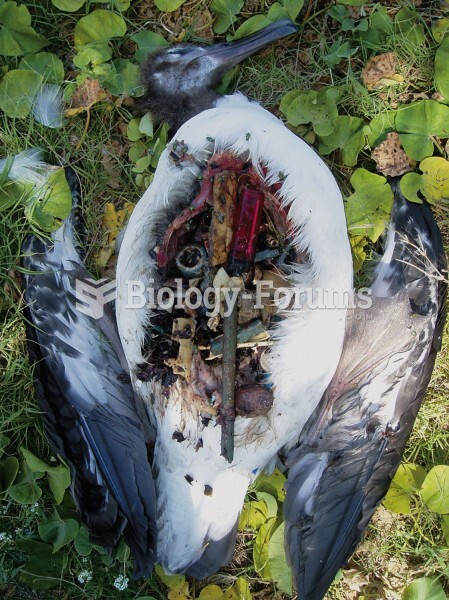
This topic contains a solution. Click here to go to the answer
|
|
|
Did you know?
Cytomegalovirus affects nearly the same amount of newborns every year as Down syndrome.
Did you know?
There are actually 60 minerals, 16 vitamins, 12 essential amino acids, and three essential fatty acids that your body needs every day.
Did you know?
The lipid bilayer is made of phospholipids. They are arranged in a double layer because one of their ends is attracted to water while the other is repelled by water.
Did you know?
Drying your hands with a paper towel will reduce the bacterial count on your hands by 45–60%.
Did you know?
Drug-induced pharmacodynamic effects manifested in older adults include drug-induced renal toxicity, which can be a major factor when these adults are experiencing other kidney problems.