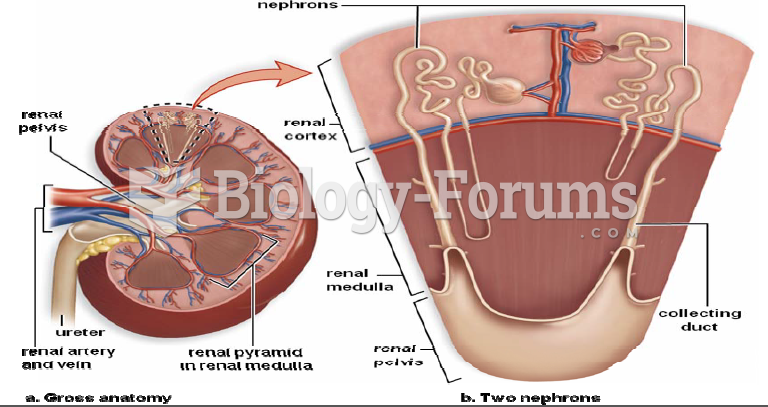
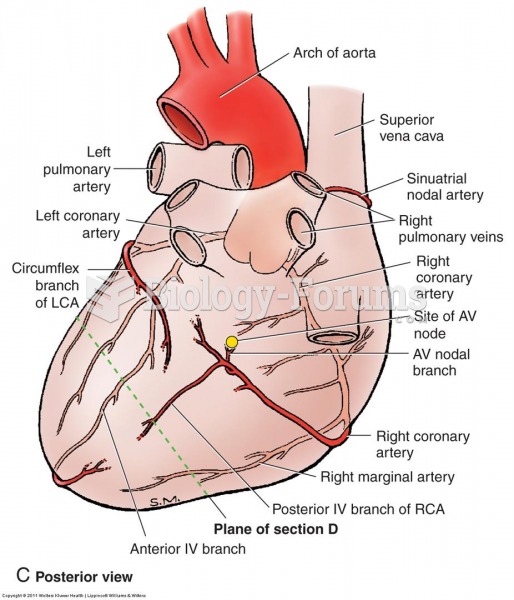
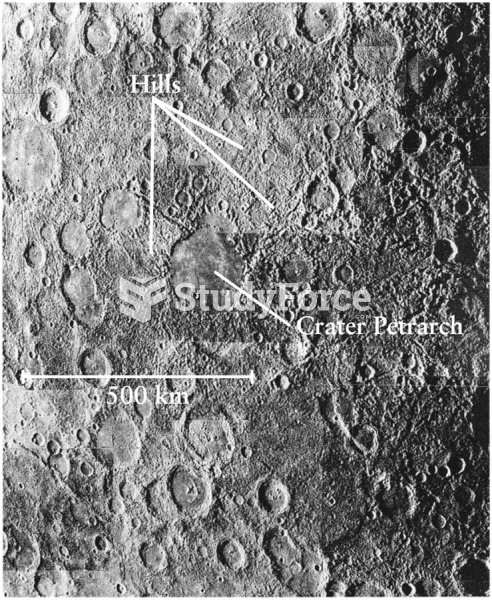
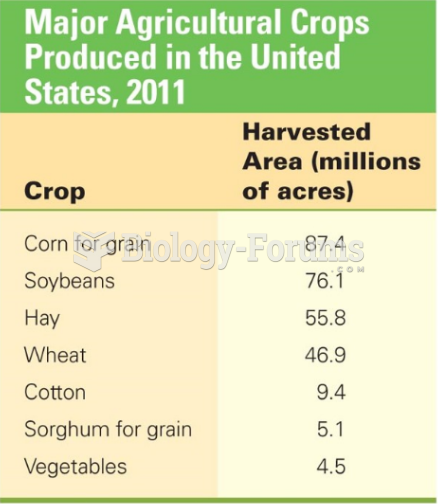
Answer to Question 1
Answer:
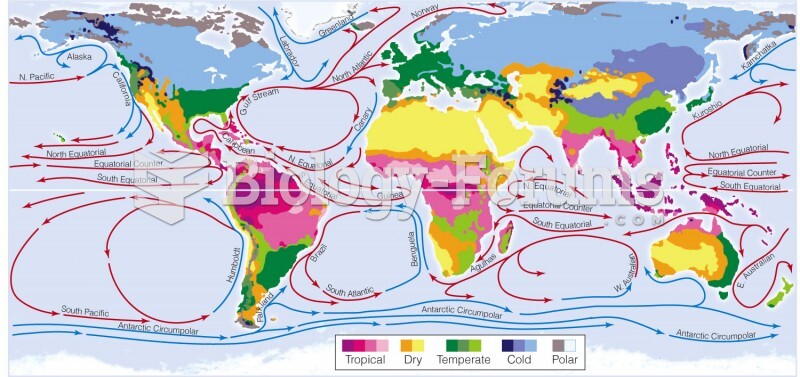
a. The University of Iowa studies explored three leadership styles. The autocratic style leader tends to centralize authority, dictate work methods, make unilateral decisions, and limit employee participation. The democratic style leader tends to involve employees in decision making, delegate authority, encourage participation in deciding work methods and goals, and use feedback as teaching moments. The laissez-faire style leader gives the group complete freedom to make decisions and complete the work in whatever way it sees fit. The research of Lewin and his associates seemed to indicate that the democratic style contributed to both good quantity and quality of work.
b. The Ohio State studies identified two dimensions of leader behavior. Initiating structure is the extent to which a leader defined and structured his role and the roles of group members in the search for goal attainment, including behavior that involved attempts to organize work, work relationships, and goals. Consideration is the extent to which a leader has job relationships characterized by mutual trust and respect for group members' ideas and feelings. A leader who was high in consideration helped group members with personal problems, was friendly and approachable, and treated all group members as equals. He showed concern for his followers' comfort, well-being, status, and satisfaction.
c. University of Michigan researchers came up with two dimensions of leadership behavior. Employee oriented leaders emphasized interpersonal relationships, took a personal interest in their followers, and accepted individual differences among group members. The production oriented leaders tended to emphasize the technical aspects of the job, were concerned mainly with accomplishing their group's tasks, and regarded group members as a means to that end. The researchers concluded leaders who were employee oriented were associated with high group productivity and high job satisfaction.
Answer to Question 2
Answer: A