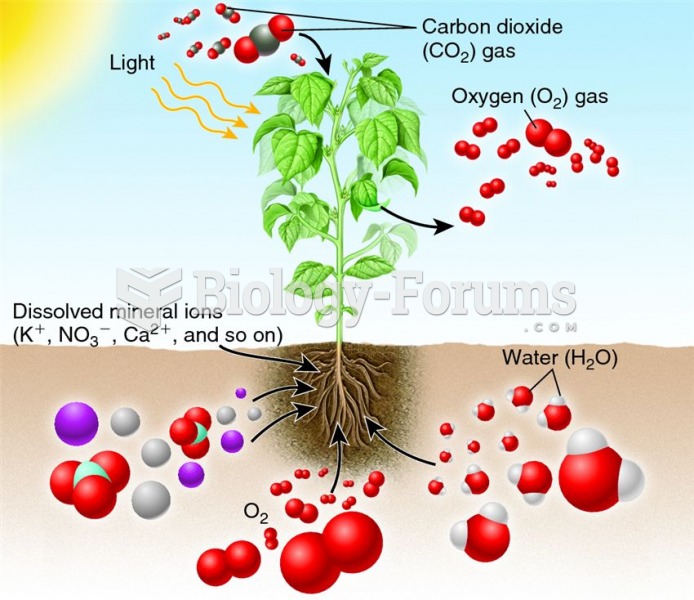
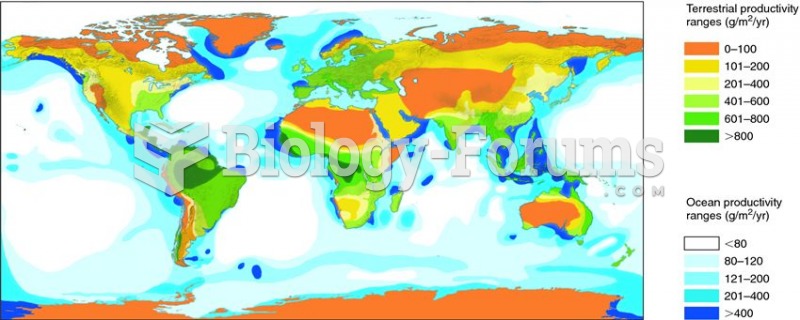
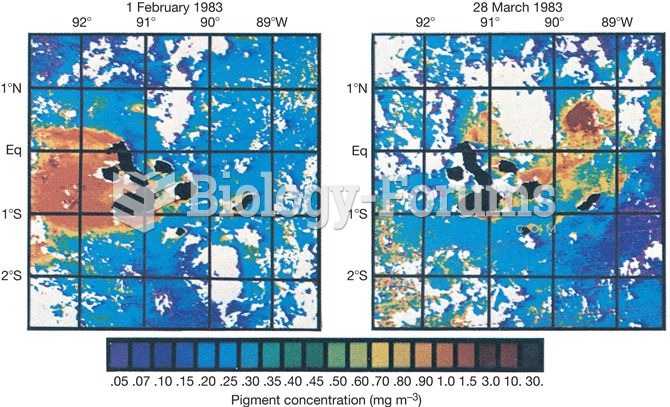
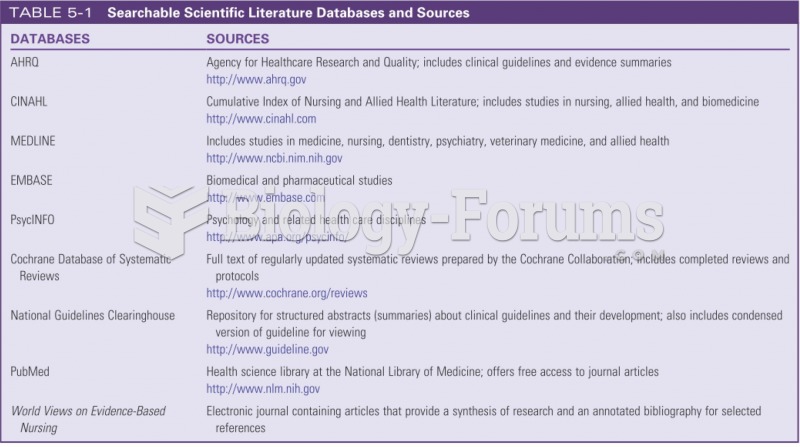
|
|
|
When taking monoamine oxidase inhibitors, people should avoid a variety of foods, which include alcoholic beverages, bean curd, broad (fava) bean pods, cheese, fish, ginseng, protein extracts, meat, sauerkraut, shrimp paste, soups, and yeast.
Alzheimer's disease affects only about 10% of people older than 65 years of age. Most forms of decreased mental function and dementia are caused by disuse (letting the mind get lazy).
Hypertension is a silent killer because it is deadly and has no significant early symptoms. The danger from hypertension is the extra load on the heart, which can lead to hypertensive heart disease and kidney damage. This occurs without any major symptoms until the high blood pressure becomes extreme. Regular blood pressure checks are an important method of catching hypertension before it can kill you.
The most destructive flu epidemic of all times in recorded history occurred in 1918, with approximately 20 million deaths worldwide.
Allergies play a major part in the health of children. The most prevalent childhood allergies are milk, egg, soy, wheat, peanuts, tree nuts, and seafood.