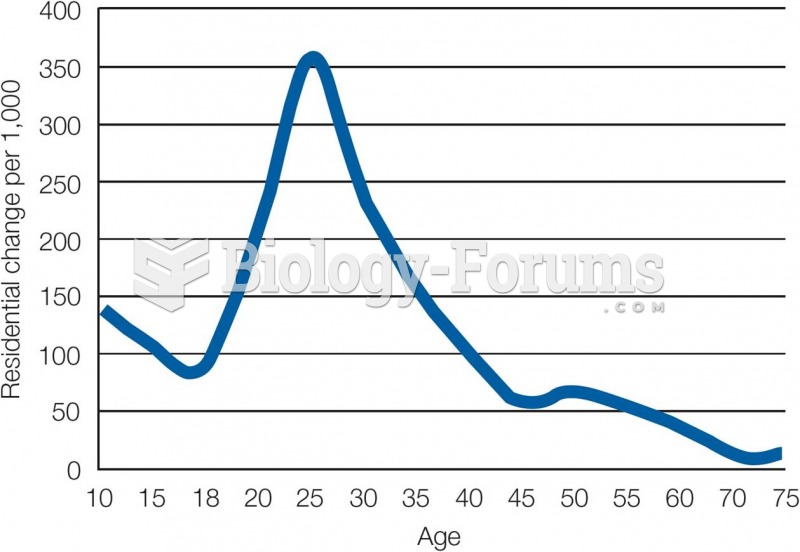
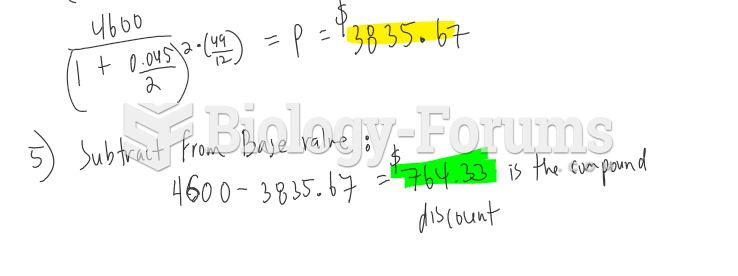Answer to Question 1
A
Answer to Question 2
The five forms are simple structure, machine bureaucracy, professional bureaucracy, divisional structure, and adhocracy.
The simple structure is appropriate for small, entrepreneurial organizations with a centralized decision maker. It can respond quickly to changes in the environment.
The machine bureaucracy is characterized by many rules and procedures and a high degree of work specialization, such as many government agencies. Decision-making is concentrated at the top. These organizations are good at performing routine, standardized tasks, in a stable environment.
The professional bureaucracy contains a large number of highly trained professionals with specialized skills, such as hospitals. Decision-making rests with these professionals. These organizations are fit for environments with many non-routine problems.
The divisional structure is typical of very large organizations. They are sets of autonomous units coordinated by a central headquarters. These organizations allow their units to concentrate on the issues of each of the separate businesses included.
The adhocracy form utilizes teamwork to a large degree, and is typically smaller and less formal than the machine bureaucracy, professional bureaucracy, and divisional forms. It is the most organic of the forms. Decision-making is often shared. This form fits best when the environment is changing rapidly and unpredictably, and innovation is required.