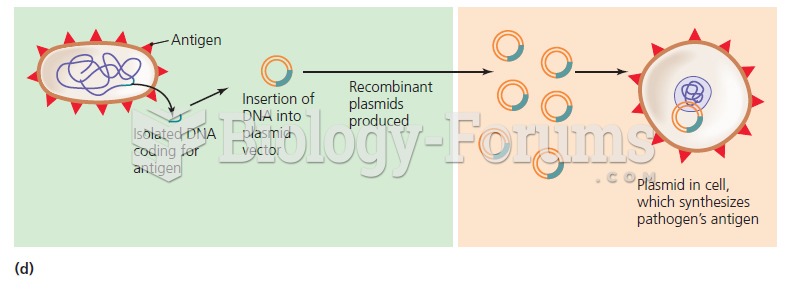
Answer to Question 1
Mediating technology is characterized by a work process in which input, conversion, and output activities can be performed independently of one another. Mediating technology is based on pooled task interdependence. One common strategy for improving organizational performance for an organization operating a mediating technology is to obtain more business from existing customers and attract new customers by increasing the number of products it offers. Mediating technology is relatively inexpensive to operate and manage. Costs are low because organizational activities are controlled by standardization. Bureaucratic rules are used to specify how the activities of different departments should be coordinated, and SOPs control the way a department operates to ensure its activities are compatible with those of other departments.
Answer to Question 2
The four types of technologies identified by Perrow on the basis of task variability and task analyzability are:
1. Routine manufacturing: Routine manufacturing is characterized by low task variability and high task analyzability. Few exceptions are encountered in the work process, and when an exception does occur, little search behavior is required to deal with it. Mass production is representative of routine technology.
2. Craftswork: With craft technology, task variability is low (only a narrow range of exceptions is encountered), and task analyzability is also low (a high level of search activity is needed to find a solution to problems). Employees in an organization using this kind of technology need to adapt existing procedures to new situations and find new techniques to handle existing problems more effectively.
3. Engineering production: With engineering production technology, task variability is high and task analyzability is high. The number or variety of exceptions that workers may encounter in the task is high, but finding a solution is relatively easy because well-understood standard procedures have been established to handle the exceptions.
4. Nonroutine research technology: Nonroutine research technology is characterized by high task variability and low task analyzability and is the most complex and least routine of the four technologies in Perrow's classification. Tasks are complex because not only is the number of unexpected situations large, but search activity is high. Each new situation creates a need to expend resources to deal with it.