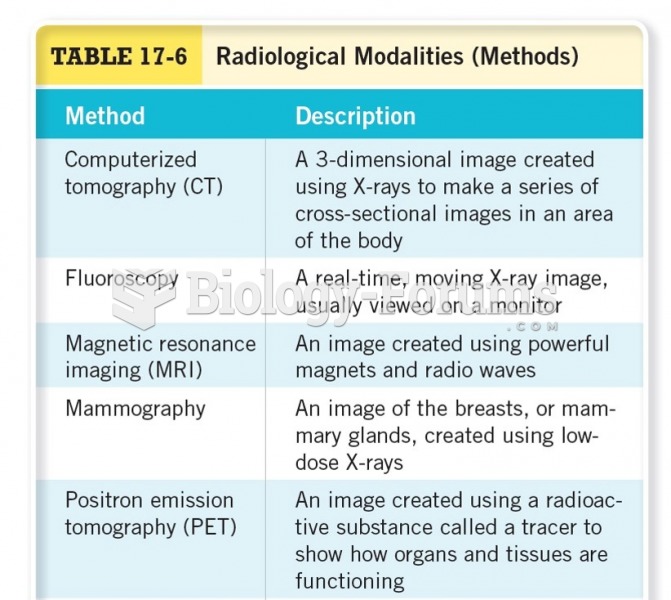
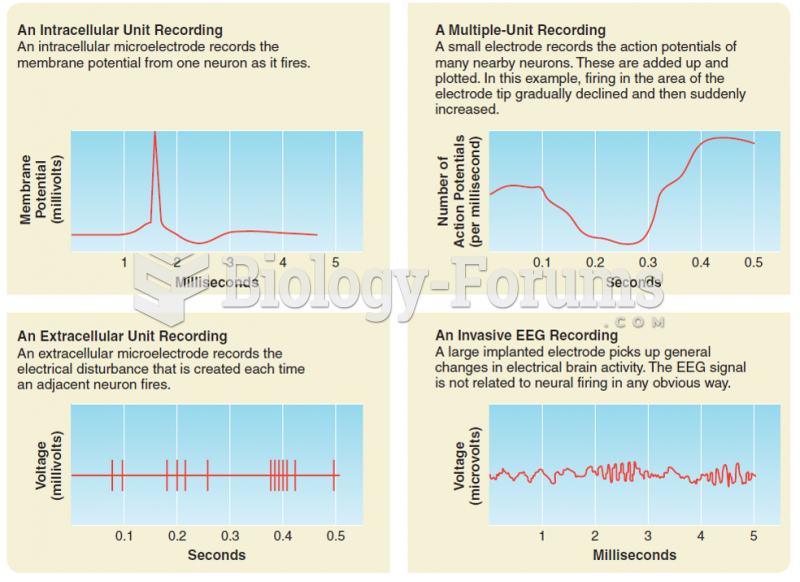
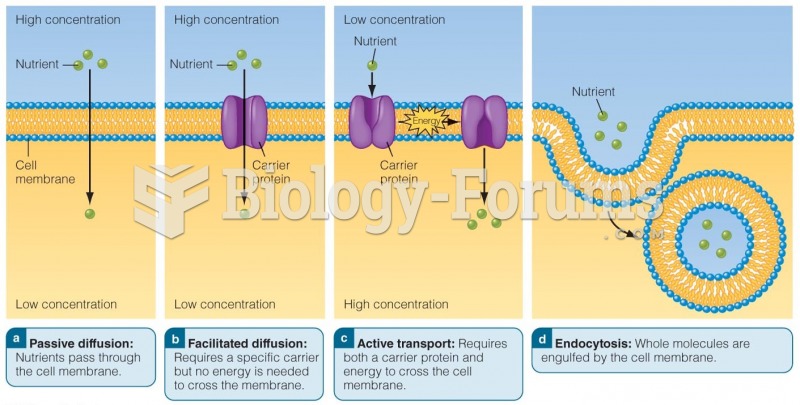
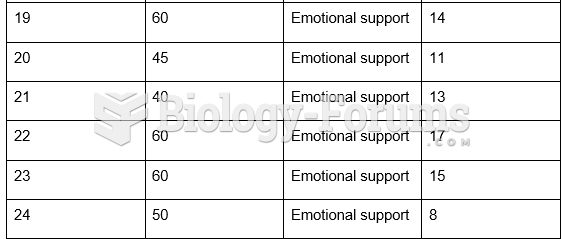
Answer to Question 1
Export/import financing methods designed to reduce risks include advance payment, documentary collection, letter of credit, and open account.
Advance Payment-Export/import financing in which an importer pays an exporter for merchandise before it is shipped is called advance payment. This method of payment is common when two parties are unfamiliar with each other, the transaction is relatively small, or the buyer is unable to obtain credit because of a poor credit rating at banks. Payment normally takes the form of a wire transfer of money from the bank account of the importer directly to that of the exporter. Although prior payment eliminates the risk of nonpayment for exporters, it creates the complementary risk of nonshipment for importersimporters might pay for goods but never receive them. Thus advance payment is the most favorable method for exporters but the least favorable for importers.
Documentary Collection-Export/import financing in which a bank acts as an intermediary without accepting financial risk is called documentary collection. This payment method is commonly used when there is an ongoing business relationship between two parties.
Letter of Credit-Export/import financing in which the importer's bank issues a document stating that the bank will pay the exporter when the exporter fulfills the terms of the document is called letter of credit. A letter of credit is typically used when an importer's credit rating is questionable, when the exporter needs a letter of credit to obtain financing, and when a market's regulations require it.
Open Account-Export/import financing in which an exporter ships merchandise and later bills the importer for its value is called open account. Because some receivables may not be collected, exporters should reserve shipping on open account only for their most trusted customers. This payment method is often used when the parties are very familiar with each other or for sales between two subsidiaries within an international company. The exporter simply invoices the importer (as in many domestic transactions), stating the amount and date due. This method reduces the risk of nonshipment faced by the importer under the advance payment method.
Answer to Question 2
TRUE