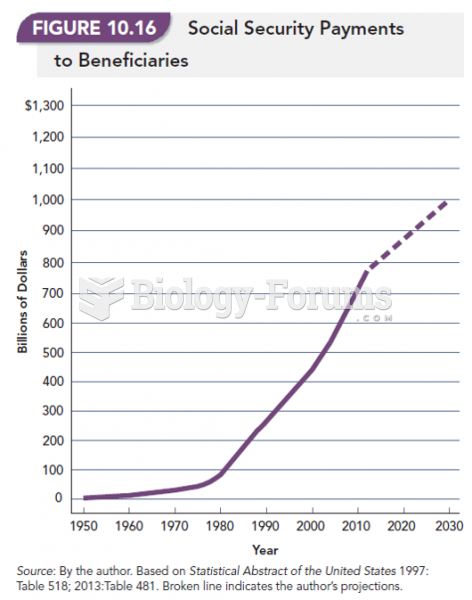
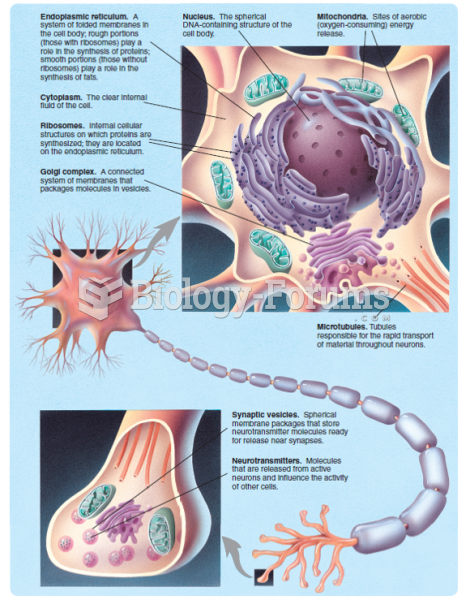
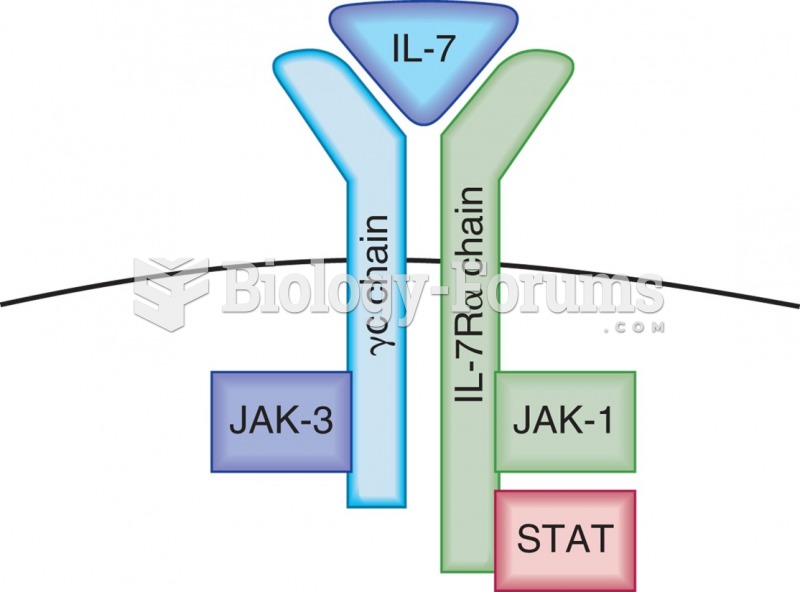
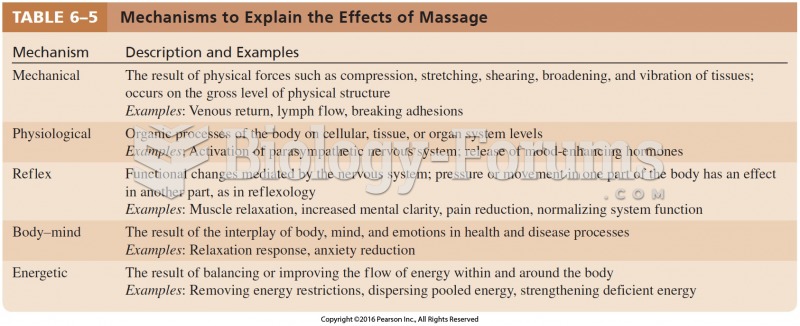
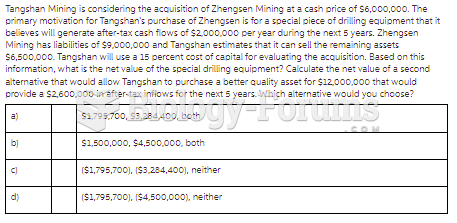
Answer to Question 1
A country's balance of payments is a national accounting system that records all payments to entities in other countries and all receipts coming into the nation. International transactions that result in payments (outflows) to entities in other nations are reductions in the balance of payments accounts and are therefore recorded with a minus sign. International transactions that result in receipts (inflows) from other nations are additions to the balance of payments accounts and thus are recorded with a plus sign.
Any nation's balance of payments consists of two major components-the current account and capital account. The current account is a national account that records transactions involving the import and export of goods and services, income receipts on assets abroad, and income payments on foreign assets inside the country. The merchandise account includes exports and imports of tangible goods such as computer software, electronic components, and apparel. The services account includes exports and imports of services such as tourism, business consulting, and banking services. Suppose a company in the United States receives payment for consulting services provided to a company in another country. The receipt is recorded as an export of services and assigned a plus sign in the services account in the balance of payments.
The capital account is a national account that records transactions involving the purchase or sale of assets. Suppose a U.S. citizen buys shares of stock in a Mexican company on Mexico's stock market. The transaction would show up on the capital accounts of both the United States and Mexico-as an outflow of assets from the United States and an inflow of assets to Mexico. Conversely, suppose a Mexican investor buys real estate in the United States. That transaction also shows up on the capital accounts of both nations-as an inflow of assets to the United States and as an outflow of assets from Mexico.
Answer to Question 2