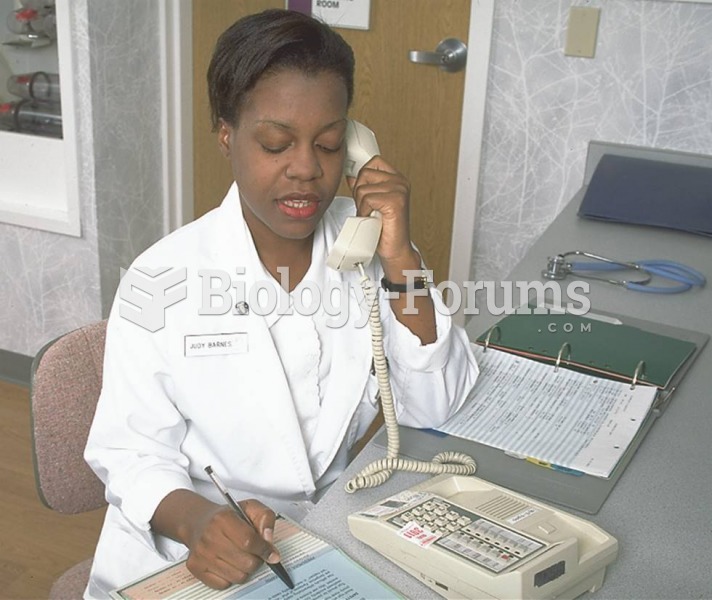
|
|
|
Essential fatty acids have been shown to be effective against ulcers, asthma, dental cavities, and skin disorders such as acne.
About one in five American adults and teenagers have had a genital herpes infection—and most of them don't know it. People with genital herpes have at least twice the risk of becoming infected with HIV if exposed to it than those people who do not have genital herpes.
Prostaglandins were first isolated from human semen in Sweden in the 1930s. They were so named because the researcher thought that they came from the prostate gland. In fact, prostaglandins exist and are synthesized in almost every cell of the body.
Adult head lice are gray, about ? inch long, and often have a tiny dot on their backs. A female can lay between 50 and 150 eggs within the several weeks that she is alive. They feed on human blood.
The Romans did not use numerals to indicate fractions but instead used words to indicate parts of a whole.