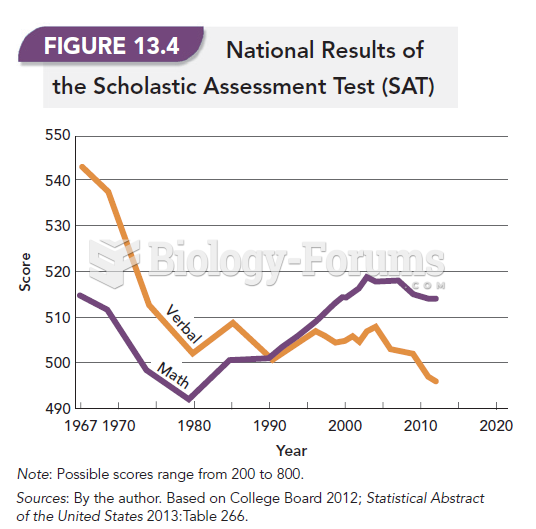
Answer to Question 1
Google makes frequent changes to their search algorithms to improve search results and user experience. Google, for instance, reportedly makes over 600 search engine changes in a year. Most are small unannounced tweaks. Recent major changes have included Panda, Penguin, Hummingbird, Knowledge Graph, and an unnamed algorithm that has been nicknamed Mobilegeddon. Panda was introduced in 2011 in an effort to weed out low quality sites from search results. Those sites with thin content, duplicate content, content copied from elsewhere on the Web, and content that did not attract high-quality hits from other sources were systematically pushed down in the search results.
Google introduced Penguin in 2012 to punish websites and their SEO marketing firms who were manipulating links to their site in order to improve their rankings. The Google search engine rewards sites that have links from many other sites. What some marketers discovered is that Google could not tell the quality of these back links, and they began to manufacture links by putting their clients onto list sites, creating multiple blogs to link to their clients' site, and paying others to link to their clients' sites. Penguin evaluates the quality of links to a site, and pushes down in the rankings those sites that have poor-quality back links.
Google introduced Hummingbird in September 2013. Rather than evaluate each word separately in a search, Google's semantically informed Hummingbird will try to evaluate an entire sentence. Semantic search more closely follows conversational search, or search as you would ordinarily speak it to another human being.
Google introduced Knowledge Graph in 2012 as an effort to anticipate what you might want to know more about as you search on a topic or answer questions you might not thought of asking. Since 2013, results of Knowledge Graph appear on the right of the screen and contain more information about the topic or person you are searching on. Not all search terms have a Knowledge Graph result. Google displays information based on what other users have searched for in the past, as well as its database on over 500 million objects (people, places, and things), and some 18 billion facts.
In 2015, Google released a new algorithm update (nicknamed Mobilegeddon) that made the mobile-friendliness of websites a much stronger ranking factor for mobile searches. Websites that are not optimized for mobile now have a much lower ranking in mobile search results. Starting in November 2015, Google also began lowering the search rank of mobile websites that display an ad that obscures the screen and asks users whether they would like to install the site's mobile app, on the grounds that such ads are less mobile-friendly
Answer to Question 2
B