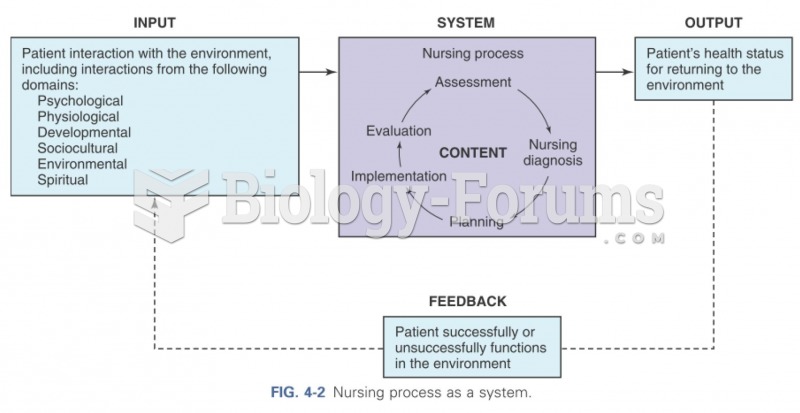
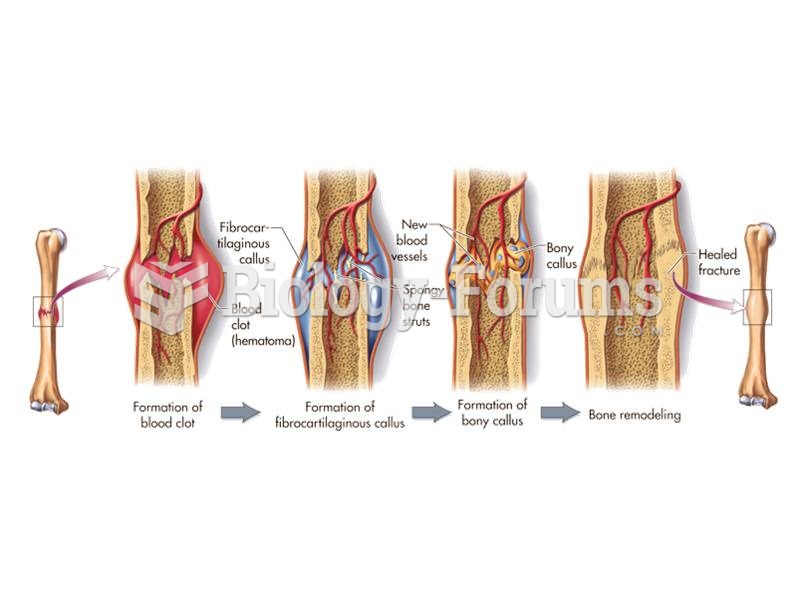
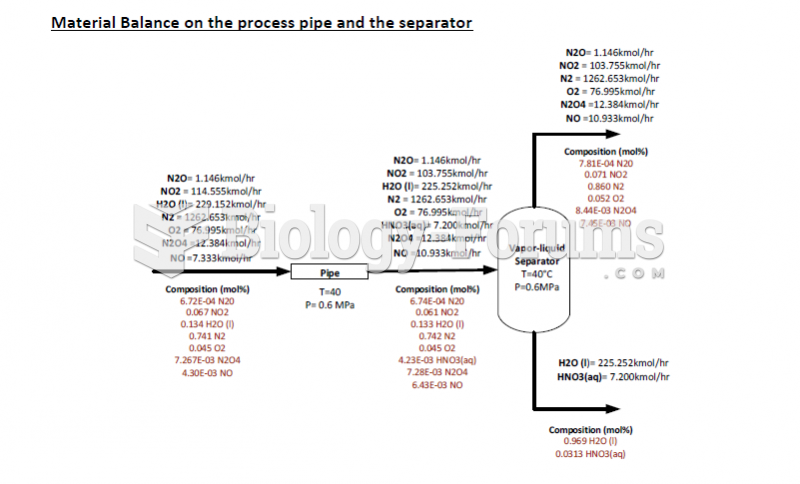
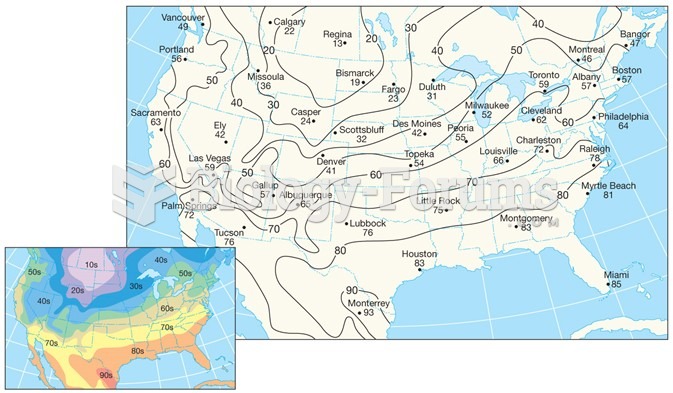
|
|
|
According to animal studies, the typical American diet is damaging to the liver and may result in allergies, low energy, digestive problems, and a lack of ability to detoxify harmful substances.
Patients should never assume they are being given the appropriate drugs. They should make sure they know which drugs are being prescribed, and always double-check that the drugs received match the prescription.
People who have myopia, or nearsightedness, are not able to see objects at a distance but only up close. It occurs when the cornea is either curved too steeply, the eye is too long, or both. This condition is progressive and worsens with time. More than 100 million people in the United States are nearsighted, but only 20% of those are born with the condition. Diet, eye exercise, drug therapy, and corrective lenses can all help manage nearsightedness.
Cucumber slices relieve headaches by tightening blood vessels, reducing blood flow to the area, and relieving pressure.
Oliver Wendell Holmes is credited with introducing the words "anesthesia" and "anesthetic" into the English language in 1846.