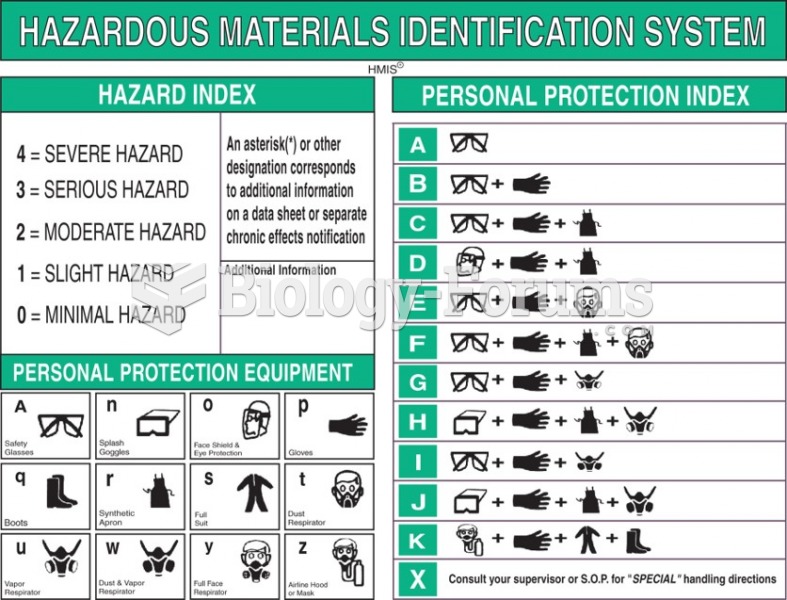
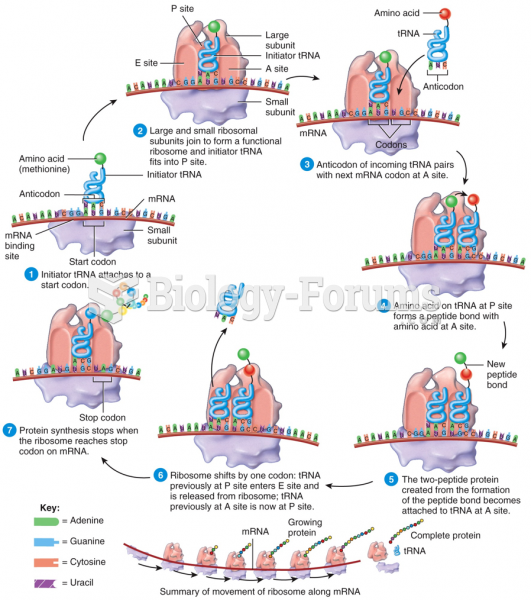
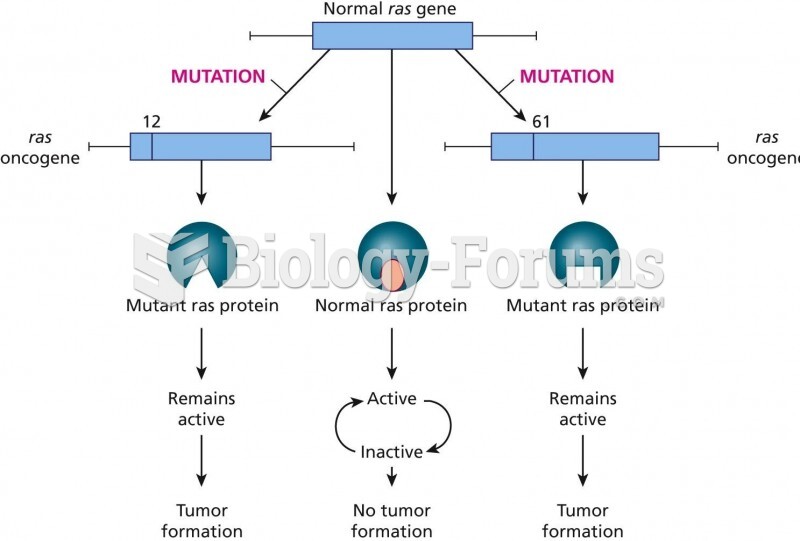
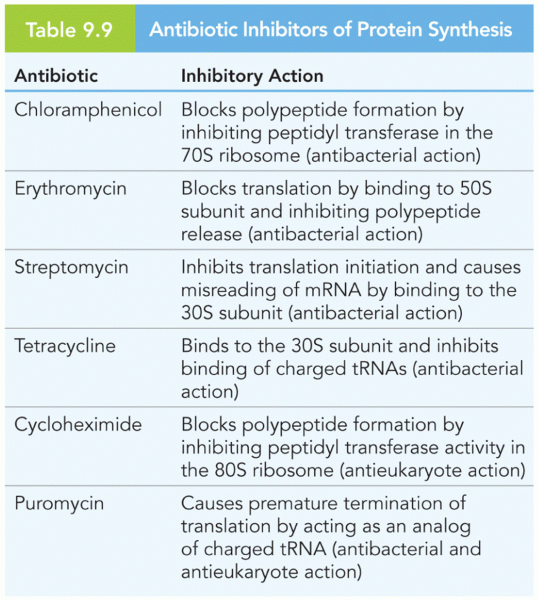
|
|
|
In most climates, 8 to 10 glasses of water per day is recommended for adults. The best indicator for adequate fluid intake is frequent, clear urination.
Computer programs are available that crosscheck a new drug's possible trade name with all other trade names currently available. These programs detect dangerous similarities between names and alert the manufacturer of the drug.
Thyroid conditions may make getting pregnant impossible.
Approximately 15–25% of recognized pregnancies end in miscarriage. However, many miscarriages often occur before a woman even knows she is pregnant.
Hip fractures are the most serious consequences of osteoporosis. The incidence of hip fractures increases with each decade among patients in their 60s to patients in their 90s for both women and men of all populations. Men and women older than 80 years of age show the highest incidence of hip fractures.