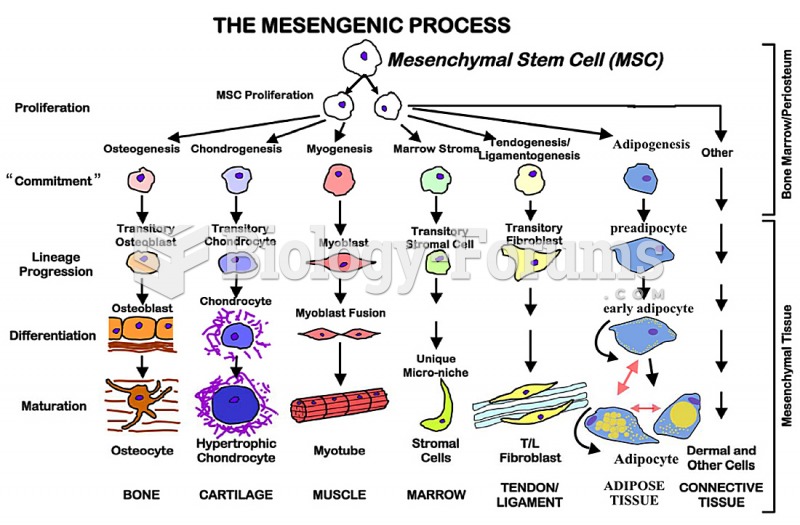
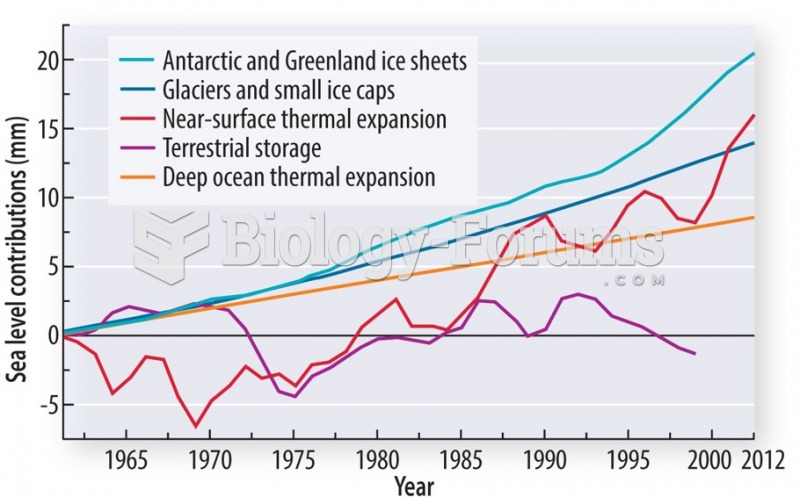
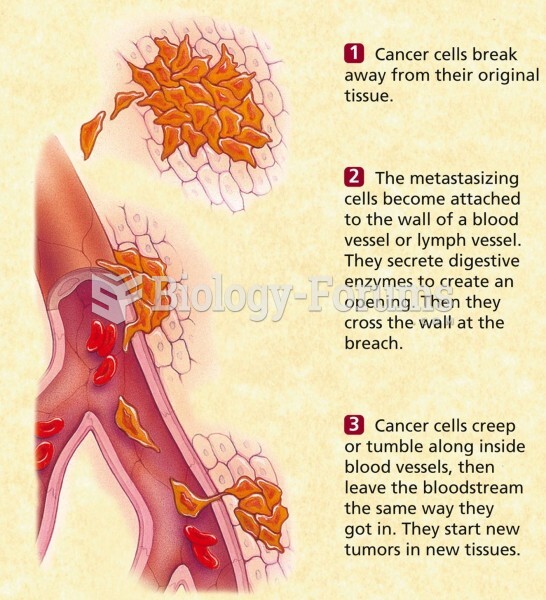
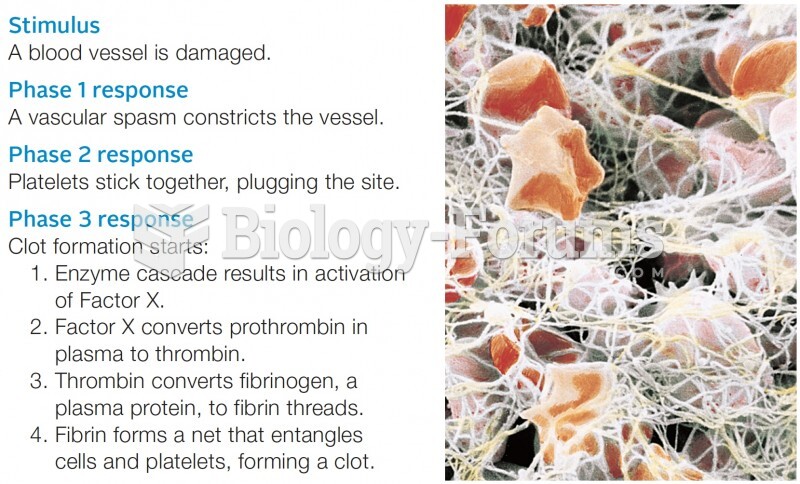
|
|
|
No drugs are available to relieve parathyroid disease. Parathyroid disease is caused by a parathyroid tumor, and it needs to be removed by surgery.
There are 60,000 miles of blood vessels in every adult human.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has released reports detailing the deaths of infants (younger than 1 year of age) who died after being given cold and cough medications. This underscores the importance of educating parents that children younger than 2 years of age should never be given over-the-counter cold and cough medications without consulting their physicians.
It is important to read food labels and choose foods with low cholesterol and saturated trans fat. You should limit saturated fat to no higher than 6% of daily calories.
Malaria was not eliminated in the United States until 1951. The term eliminated means that no new cases arise in a country for 3 years.