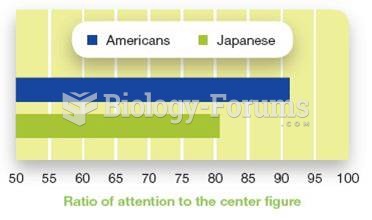
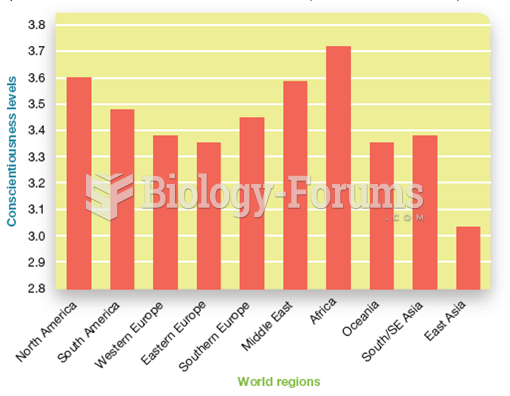
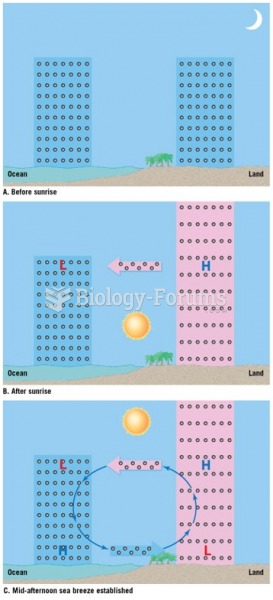
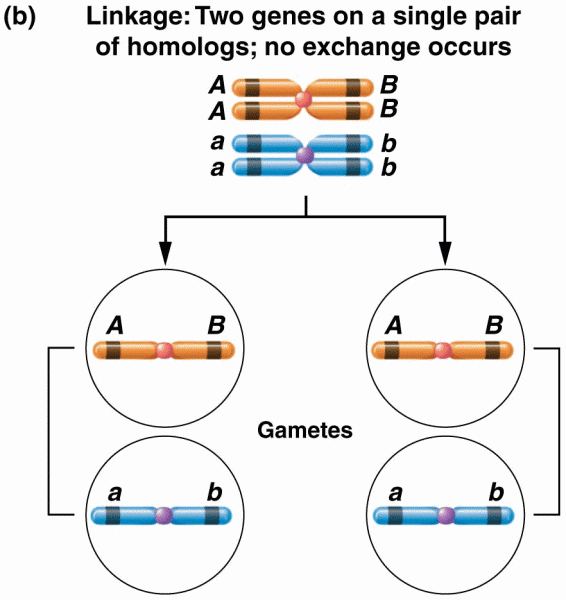
Answer to Question 1
Of the two, UTP is by far the most commonly used. UTP's cost is significantly less than STP's. Also, because STP uses more shielding to protect its internal copper wiring, it is bulky and can be difficult to work with in tight spaces. UTP, however, is very inexpensive, easy to install, and highly flexible. One potential problem with both types is a moderate risk of security violation. An unauthorized individual could, with the right equipment and opportunity, tap into the copper cabling that UTP and STP are based on. The signals that flow over the copper wire make no distinction between authorized and unauthorized taps. Security is thus a factor to be considered. UTP is far more susceptible to noise and electromagnetic interference than either coaxial or fiber-optic cabling. Also, UTP signals cannot travel as far as signals on the other cable types before they need to be boosted. Even so, due to its low cost and ease of installation, UTP is the most common medium used in data communications networks.
Answer to Question 2
First, a cable must have a conductor over which a signal can be conducted. The conductor will either be copper wire for twisted-wire pair and coaxial cables or glass or plastic strands for fiber-optic cables. For copper, the conductor, called the carrier wire, might be solid or stranded, and the conductor's diameter might be measured in inches, centimeters, or millimeters. The American Wire Gauge (AWG) is another common means for specifying the diameter of a wire conductor. For fiber-optic cables, the conductor is called the core. The core can be either a glass or plastic tube that runs through the cable. The core's diameter is measured in microns, which are millionths of a meter. Secondly, a cable's conductor has some type of insulation that is used to keep the signal in and external interferences out. For electrical wire, the insulation is usually made from some type of nonconductor, such as polyethylene. Fiber-optic insulation is called cladding. The cladding is made of a material with a lower refraction index than the core's material. The refraction index measures the ability of a material to reflect light rays. For fiber-optic cables, a cladding with a lower refraction index than the core ensures that light bounces back off the cladding and remains in the core. Finally, a cable also has some type of outer sheath, or jacket, which encases the cable's elements and keeps them together. The sheath can also serve to provide some measure of protection from environmental forces such as water, pressure, or heat.