NUTRITION, METABOLISM AND BODY TEMPERATURE REGULATION
1. The molecule that serves as the major source of readily available body fuel is:
a. fat.
b. Glucose.
c. Acetyl CoA.
d. Cellulose.
2. Which cells of the body would suffer most if glucose blood levels were to drop
drastically?
a. liver and spleen
b. intestinal and pancreatic
c. heart and lung
d. brain neurons and red blood cells
3. Dietary fats are important because:
a. they keep blood pressure normal.
b. they help the body absorb fat-soluble vitamins.
c. they contribute significantly to the health of the skin.
d. they help prevent the common cold.
4. Cholesterol, while it is not an energy molecule, has importance in the body because:
a. it is stabilizing component of the plasma membranes and is the parent molecule
of steroid hormones.
b. it helps provide essential nutrients to the brain and lungs.
c. it helps mobilize fats during periods of starvation.
d. it enters the glycolytic pathway without being altered.
5. Which of the following statements best describes complete protein?
a. derived from meat and fish only
b. meets all the minimum daily requirements for a sound diet
c. derived from legumes and other plant material
d. must meet all the body’s amino acid requirements for maintenance and
growth
6. The term metabolism is best defined as:
a. the length of time it takes to digest and absorb fats.
b. a measure of carbohydrate utilization.
c. the number of calories it takes to keep from shivering on a cold day.
d. the sum of energy produced by all the chemical reactions and mechanical work
of the body.
7. Many factors influence BMR. What is the most critical factor?
a. The way an individual metabolizes fat.
b. The way skeletal muscles break down glycogen.
c. The ratio of surface area to volume (weight) of the body.
d. An individual’s body weight.
8. The term energy output includes:
a. the energy lost as heat (60%).
b. the energy used to work (driven by ATP).
c. the energy stored in the form of glycogen.
d. All of the above are correct.
9. The primary reason elderly people should decrease their caloric intake is that:
a. their muscles begin to atrophy and require less energy.
b. their appetite begins to diminish.
c. they have a higher metabolic rate and do not need large amounts of food.
d. they spend most of the day at rest, and their food will quickly turn to fat.
10. The primary reason the elderly seem to have more negative effects from some
medications is that:
a. they often forget to take their medications as prescribed.
b. they tend to skip meals.
c. they are not exercising.
d. their livers have become less efficient at detoxifying.
11. Which of the following statements is true regarding the use of mineral oil as a
laxative by the elderly?
a. It interferes with the absorption of fat-soluble minerals.
b. It is a strong cathartic and may cause dehydration.
c. Mineral oil is often contaminated and could cause severe illness in the elderly.
d. Mineral oil is an old-fashioned laxative and should not be used by an segment
of society.
12. The term essential amino acid refers to those amino acids that:
a. the body cannot synthesize.
b. contribute to structural proteins.
c. become part of the metabolic reserves.
d. are stored.
13. Which of the following bests defines negative nitrogen balance?
a. Protein breakdown exceeds protein synthesis.
b. A condition caused by having a diet low in fish and meat.
c. Negative nitrogen balance is normal and is a way of maintaining homeostasis.
d. Occurs when amino acids are broken down by liver enzymes and carried to the
bloodstream.
14. When proteins undergo deamination, a substance found in the urine is:
a. steroids.
b. ammonia.
c. acetyl CoA.
d. ketone bodies.
15. While the amount of protein required in the diet varies depending on age, size, and needs,
the daily recommendation is approximately:
a. 0.4 g/kg body weight.
b. 0.8 g/kg body weight.
c. 10 g/kg body weight.
d. 13 g/kg body weight.
16. It is important to ensure that your diet is adequately rich in vitamins because:
a. vitamins provide protection against the common cold.
b. very few foods contain vitamins.
c. most vitamins are coenzymes needed to help the body utilize essential nutrients.
d. all vitamins are water-soluble and pass out of the body too quickly to ensure
utilization.
17. Oxidation-reduction reactions are catalyzed by which of the following enzymes?
a. dehydrogenases and oxidases
b. kinases and phophorylases
c. phosphatases and kinases
d. synthetases and lipases
18. Of all the minerals required by the human body, ______ and _______ account for three-
quarters of the total.
a. zinc; selenium
b. potassium; sodium
c. sulfur; chloride
d. calcium; phosphorus
19. A diet rich in minerals would include which of the following foods?
a. fats, sugars, and apples
b. refined cereals, grains and rye bread
c. legumes, milk and pork
d. eggs, bacon, and pizza
20. Which of the following food groups may be considered complete proteins?
a. corn, cottonseed oil, soy oil, and wheat germ
b. lima beans, kidney beans, nuts, and cereals
c. egg yolk, fish roe, and grains.
d. eggs, milk, yogurt, meat, and fish
21. Anabolism includes reactions in which:
a. carbohydrate utilization increases.
b. larger molecules or structures are built from smaller ones.
c. structural proteins are used as a potential energy source.
d. ketone bodies are formed.
22. Catabolism involves processes that:
a. cause a decline in circulating ketone bodies.
b. mobilize fat during the postabsorptive state.
c. break down complex structures to simpler ones.
d. elevate glucagons levels.
23. The primary function of cellular respiration is to:
a. determine the amount of heat needed by the human body.
b. provide the body with adequate amounts of vitamins and minerals.
c. efficiently monitor the energy needs of the body.
d. generate ATP, which traps some of the chemical energy of food molecules in its
high-energy bonds.
24. Which of the following nutrients yield the highest amount of energy per gram when
metabolized?
a. fats
b vitamins and minerals
c foods and beverages high in caffeine
d proteins
25. The process of breaking triglycerides down into glycerol and fatty acids is known as:
a. gluconeogenesis.
b. fat utilization
c. carbohydrate utilization.
d. lipolysis.
26. Which of the following mechanisms yields the most energy that is captured in ATP bonds
during cellular respiration?
a. oxidative phosphorylation
b. substrate-level phosphorylation
c. oxidation-reduction reactions
d. oxidation reactions
27. Lipogenesis occurs when:
a. there is a shortage of fatty acids.
b. glucose levels drop slightly.
c. excess proteins are transported through the cell membrane.
d. cellular ATP and glucose levels are high.
28. Oxidative deamination takes place in the:
a. liver.
b. muscles.
c. kidneys.
d. blood.
29. Transamination is the process whereby the amine group of an amino acid is:
a. transferred to acetyl CoA.
b. converted to urea.
c. transferred to a keto acid.
d. converted to ammonia.
30. Glycogen is formed in the liver during the:
a. postabsorptive state.
b. absorptive state.
c. starvation period.
d. period when the metabolic rate is lowest.
31. Which of the following is a normal consequence of the activation of the heat-promoting
center?
a. release of norepinephrine
b. shivering
c. increase in thryroxine production
d. All of the above are correct.
32. Which of the following does not occur in the mitochondria?
a. electron transport
b. glycolysis
c. Krebs cycle
d. formation of malic acid from fumaric acid
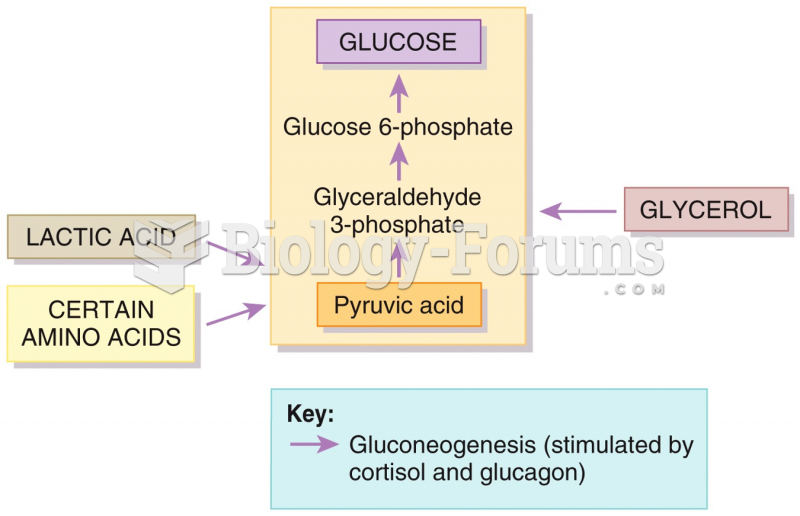
33. Gluconeogenesis is the process in which:
a. glycogen is broken down to release glucose.
b. glucose is formed from noncarbohydrate precursors.
c. glycogen is formed.
d. glucose is converted into carbon dioxide and water.
34. Deamination is a chemical process in which:
a. protein is synthesized.
b. amino acids are buffered in the kidney.
c. the amine group is removed from the amino acid.
d. amino acids are broken down for energy.
35. Glycolysis is best defined as the:
a. conversion of glucose into carbon dioxide and water.
b. conversion of glucose into two molecules of pyruvic acid.
c. conversion of pyruvic acid into carbon dioxide and water.
d. formation of sugar.
36. Among the conditions required for measuring the basal metabolic rate is:
a. being in an absorptive state.
b. remaining in an upright position.
c. keeping the room temperature between 20 and 25 degrees. C.
d. None of the above are correct.
37. The primary function of carbohydrates is to:
a. contribute to cell structure.
b. maintain a large storehouse of glycogen.
c. maintain energy production within the cells.
d. form functional molecules like hemoglobin and cytochromes.
38. During normal conditions, proteins are essential to the body for all the following except:
a. production of energy.
b. production of some hormones.
c. production of enzymes, clotting factors, antibodies.
d. formation of functional molecules like hemoglobin and cytochromes.
39. Conditions that promote the oxidative Deamination of amino acids include:
a. lack of one or more of the essential amino acids.
b. inadequate fat or carbohydrate calories to provide adequate ATP formation.
c. excessive amounts of proteins in the diet.
d. All of the above are correct.
40. When a person’s hypothalamic thermostat is set to a higher level and the actual body
temperature is below that level, the person may:
a. pant.
b. exhibit vasodilation.
c. perspire heavily.
d. shiver.
41. Which of the following is not true of beta oxidation?
a. It occurs in the mitochondrion.
b. Cleavage occurs at every second carbon.
c. It involves the anabolism of fats.
d. It yields acetic acid.
42. During aerobic respiration, electrons are passed down the electron transport chain and
_____________ is formed.
a. water
b. oxygen
c. glycogen
d. NADH2
43. If oxygen is lacking, how many net ATP are produced by the catabolism of one molecule
of glucose?
a. 1
b. 2
c. 8
d. 38
44. The most abundant dietary lipids are:
a. cholesterol.
b. phospholipids.
c. fatty acids.
d. neutral fats.
45. Loss of heat in the form of infrared waves is termed:
a. radiation.
b. convection.
c. conduction.
d. evaporation.
46. In carbohydrate metabolism, the carbohydrates:
a. are converted into fat if present in excess.
b. such as the monomer galactose are normally used to make ATP.
c. are converted into fructose by the liver before they enter into general circulation.
d. that are highly refined offer many valuable nutrients in addition to calories.
47. Prostaglandins play a role in:
a. smooth muscle contraction.
b. control of blood pressure.
c. inflammatory responses.
d. All of the above are correct.
48. Select the correct statement about proteins.
a. Strict vegetarians need not worry about adequate protein intake, as all vegetables
are almost perfect sources of amino acids.
b. Proteins can be synthesized in the body if most of the amino acids are present.
c. Proteins will be used for ATP synthesis if insufficient calories are ingested.
d. Catabolic steroids (hormones) accelerate the rate of protein synthesis.
49. Vitamins are organic compounds. They:
a. are classified as water-soluble or protein-soluble classes.
b. are also call provitamins if used in catalytic reactions.
c. often function as coenzymes to assist in catalysis.
d. All of the above are correct.
50. Minerals are substances that cannot be used for fuel. They:
a. include substances like sodium, chloride, and phosphorus.
b. are the major electrolytes in the blood.
c. help maintain water balance.
d. All of the above are correct.
51. Select the correct statement.
a. Anabolism is the process of breaking down large substances into smaller ones.
b. Cellular respiration is a catabolic process.
c. During oxidation reactions, substances gain electrons.
d. During reduction reactions, substances lose electrons.
52. Oxidation reduction reactions;
a. utilize dehydrogenases.
b. require oxidases.
c. are always coupled together.
d. All of the above are correct.
53. Vitamin __________ is present in the body as coenzyme FAD and FMN and is a
component of amino acid oxidase.
a. A
b. D
c. B1
d. B2
54. The pickup molecule for the Krebs cycle is __________ acid.
a. isocitric
b. fumaric
c. oxaloacetic
d. malic
55. As the body progresses from the absorptive to postabsorptive state only the __________
continues to burn glucose while every other organ in the body switches to fatty acids.
a. liver
b. brain
c. pancreas
d. spleen
56. Which of the following is most correct?
a. Most of the ATP are produced by substrate-level phosphorylation.
b. Oxidation of FADH2 yields four ATP via oxidative phosphorylation.
c. Glycolysis relies on substrate-level phosphorylation for the four ATP produced in
this pathway.
d. Most of the ATP are produced directly in the Krebs cycle.
57. In gluconeocogenesis, amino acids and _______ are converted to glucose.
a. glycerol
b. glycogen
c. glyceraldehydes
d. glucagons
58. Which of the following is most correct?
a. A 24-carbon fatty acid yields 6 acetyl CoA molecules.
b. The total yield from the complete oxidation of a 10-carbon fatty acid would be 60
ATP.
c. Lipogenesis is triglyceride synthesis.
d. Lipolysis results in the formation of triglycerides.
59. The liver synthesizes lipoproteins for cholesterol transport. Select the other function(s) of
the liver.
a. synthesizes a component essential for blood clotting.
b. synthesizes cholesterol
c. uses cholesterol to make bile components.
d. All of the above are correct.
60. In the liver, the amine group of glutamic acid is removed as ______ in the oxidative
state.
a. glyceraldehydes
b. pyruvic acid
c. ammonia
d. oxaloacetic acid