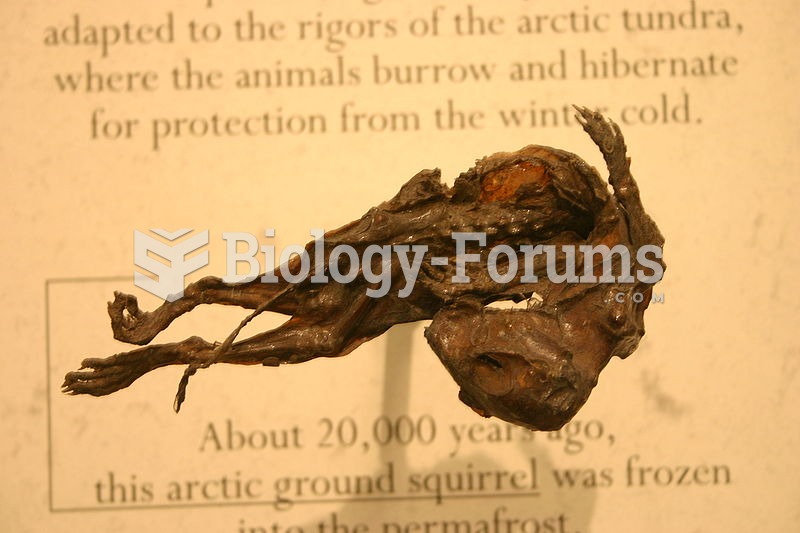
|
|
|
Drying your hands with a paper towel will reduce the bacterial count on your hands by 45–60%.
The word drug comes from the Dutch word droog (meaning "dry"). For centuries, most drugs came from dried plants, hence the name.
Cutaneous mucormycosis is a rare fungal infection that has been fatal in at least 29% of cases, and in as many as 83% of cases, depending on the patient's health prior to infection. It has occurred often after natural disasters such as tornados, and early treatment is essential.
There are more nerve cells in one human brain than there are stars in the Milky Way.
Only 12 hours after an egg cell is fertilized by a sperm cell, the egg cell starts to divide. As it continues to divide, it moves along the fallopian tube toward the uterus at about 1 inch per day.
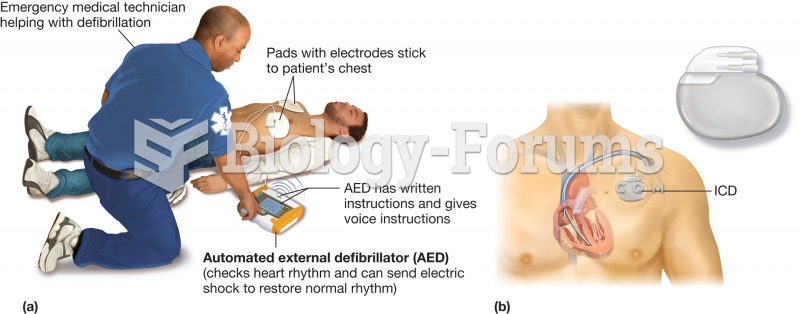 Defibrillator. Defibrillators are devices that supply a voltage charge to the heart in the hope of r
Defibrillator. Defibrillators are devices that supply a voltage charge to the heart in the hope of r
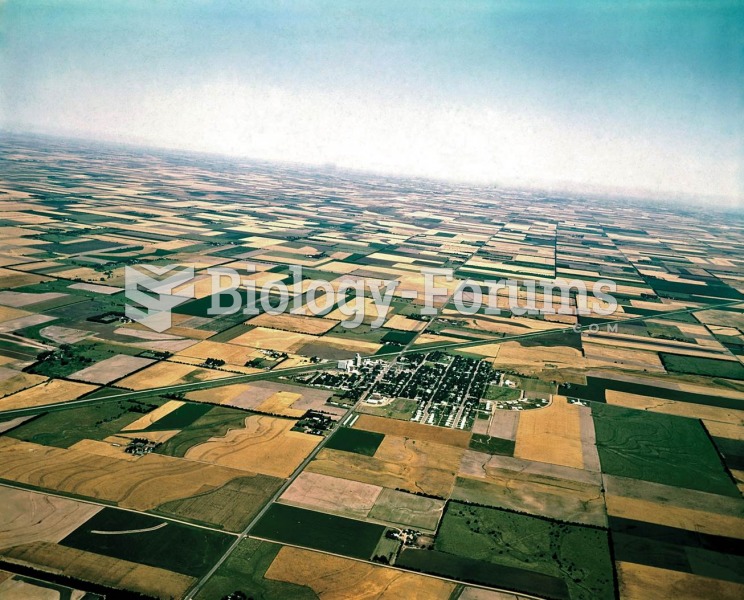 The Land Ordinance of 1785 called for surveying and dividing the Western Territories into square mil
The Land Ordinance of 1785 called for surveying and dividing the Western Territories into square mil