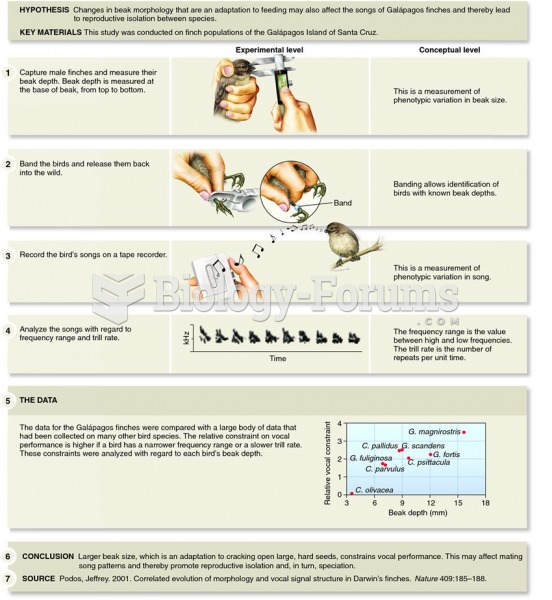
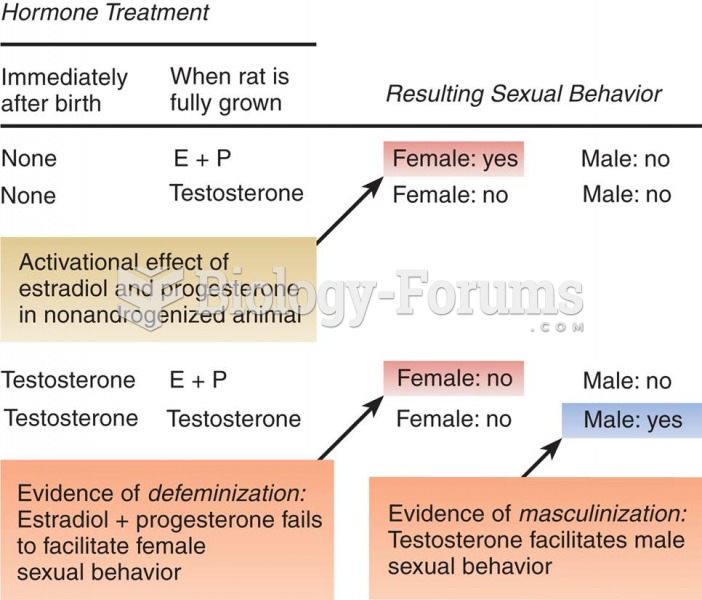
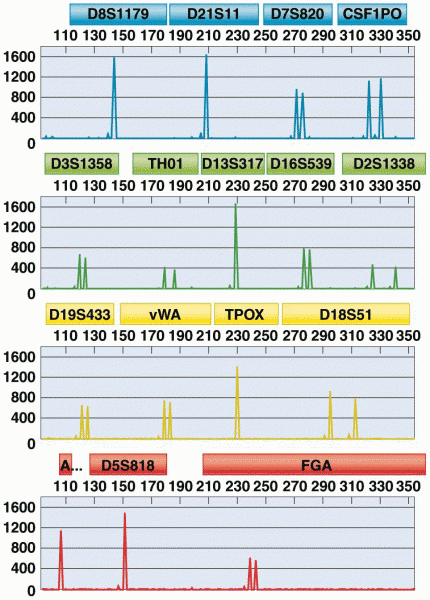
|
|
|
The average human gut is home to perhaps 500 to 1,000 different species of bacteria.
This year, an estimated 1.4 million Americans will have a new or recurrent heart attack.
The first documented use of surgical anesthesia in the United States was in Connecticut in 1844.
About one in five American adults and teenagers have had a genital herpes infection—and most of them don't know it. People with genital herpes have at least twice the risk of becoming infected with HIV if exposed to it than those people who do not have genital herpes.
There are major differences in the metabolism of morphine and the illegal drug heroin. Morphine mostly produces its CNS effects through m-receptors, and at k- and d-receptors. Heroin has a slight affinity for opiate receptors. Most of its actions are due to metabolism to active metabolites (6-acetylmorphine, morphine, and morphine-6-glucuronide).