|
|
|
Not getting enough sleep can greatly weaken the immune system. Lack of sleep makes you more likely to catch a cold, or more difficult to fight off an infection.
People who have myopia, or nearsightedness, are not able to see objects at a distance but only up close. It occurs when the cornea is either curved too steeply, the eye is too long, or both. This condition is progressive and worsens with time. More than 100 million people in the United States are nearsighted, but only 20% of those are born with the condition. Diet, eye exercise, drug therapy, and corrective lenses can all help manage nearsightedness.
It is difficult to obtain enough calcium without consuming milk or other dairy foods.
Walt Disney helped combat malaria by making an animated film in 1943 called The Winged Scourge. This short film starred the seven dwarfs and taught children that mosquitos transmit malaria, which is a very bad disease. It advocated the killing of mosquitos to stop the disease.
Giardia is one of the most common intestinal parasites worldwide, and infects up to 20% of the world population, mostly in poorer countries with inadequate sanitation. Infections are most common in children, though chronic Giardia is more common in adults.
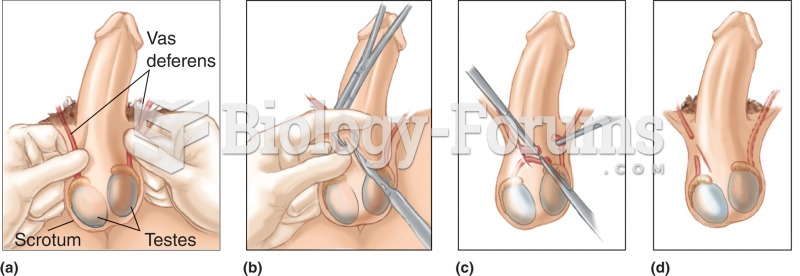 Vasectomy. (a) Vas deferens is located within the spermatic cord on both sides. (b) A small incision
Vasectomy. (a) Vas deferens is located within the spermatic cord on both sides. (b) A small incision
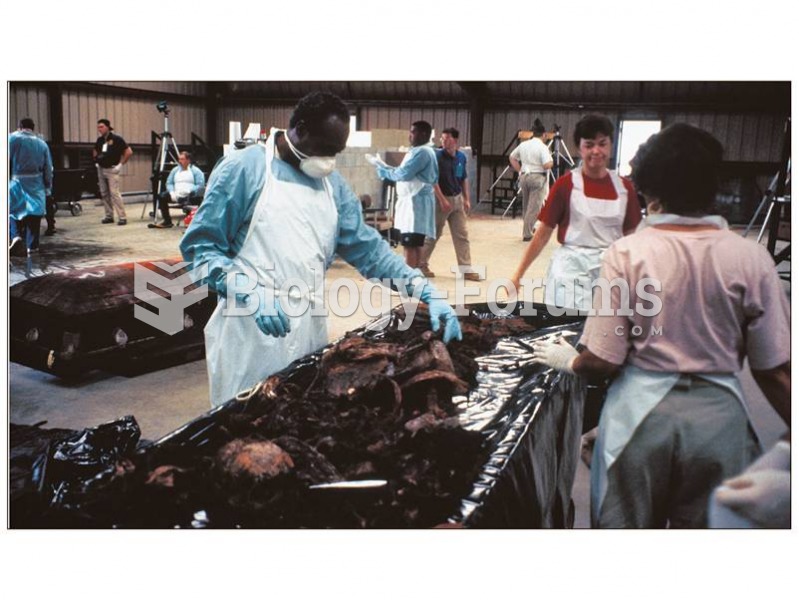 Forensic anthropologists working at a temporary morgue following the recovery of remains from a floo
Forensic anthropologists working at a temporary morgue following the recovery of remains from a floo
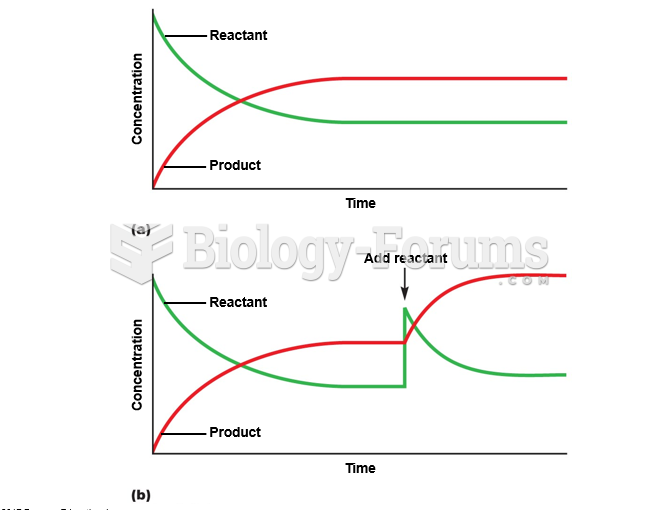
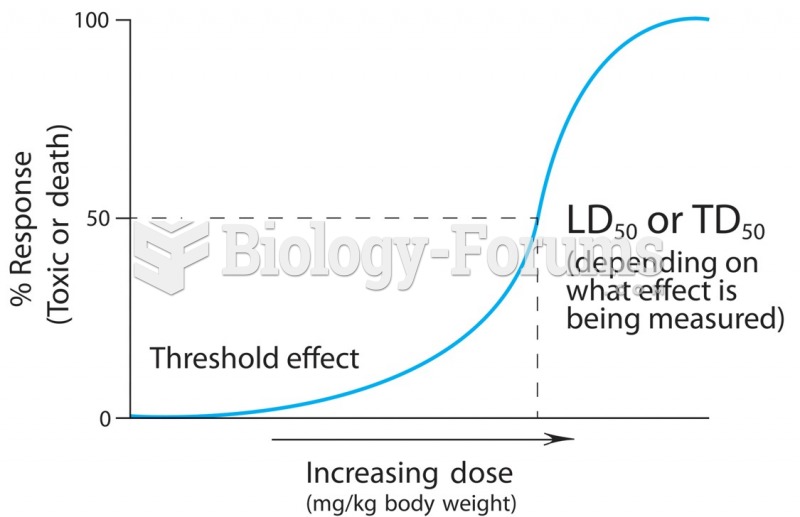 A dose-response curve describes the relationship between the quantity of the chemical entering the ...
A dose-response curve describes the relationship between the quantity of the chemical entering the ...