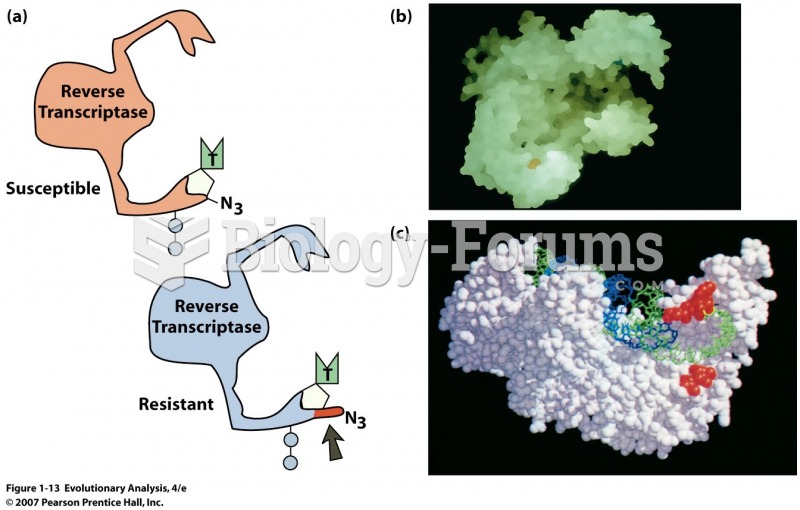
|
|
|
Aspirin is the most widely used drug in the world. It has even been recognized as such by the Guinness Book of World Records.
Pink eye is a term that refers to conjunctivitis, which is inflammation of the thin, clear membrane (conjunctiva) over the white part of the eye (sclera). It may be triggered by a virus, bacteria, or foreign body in the eye. Antibiotic eye drops alleviate bacterial conjunctivitis, and antihistamine allergy pills or eye drops help control allergic conjunctivitis symptoms.
Pope Sylvester II tried to introduce Arabic numbers into Europe between the years 999 and 1003, but their use did not catch on for a few more centuries, and Roman numerals continued to be the primary number system.
Symptoms of kidney problems include a loss of appetite, back pain (which may be sudden and intense), chills, abdominal pain, fluid retention, nausea, the urge to urinate, vomiting, and fever.
The average office desk has 400 times more bacteria on it than a toilet.