|
|
|
It is difficult to obtain enough calcium without consuming milk or other dairy foods.
Bacteria have flourished on the earth for over three billion years. They were the first life forms on the planet.
Symptoms of kidney problems include a loss of appetite, back pain (which may be sudden and intense), chills, abdominal pain, fluid retention, nausea, the urge to urinate, vomiting, and fever.
The average human gut is home to perhaps 500 to 1,000 different species of bacteria.
Children with strabismus (crossed eyes) can be treated. They are not able to outgrow this condition on their own, but with help, it can be more easily corrected at a younger age. It is important for infants to have eye examinations as early as possible in their development and then another at age 2 years.
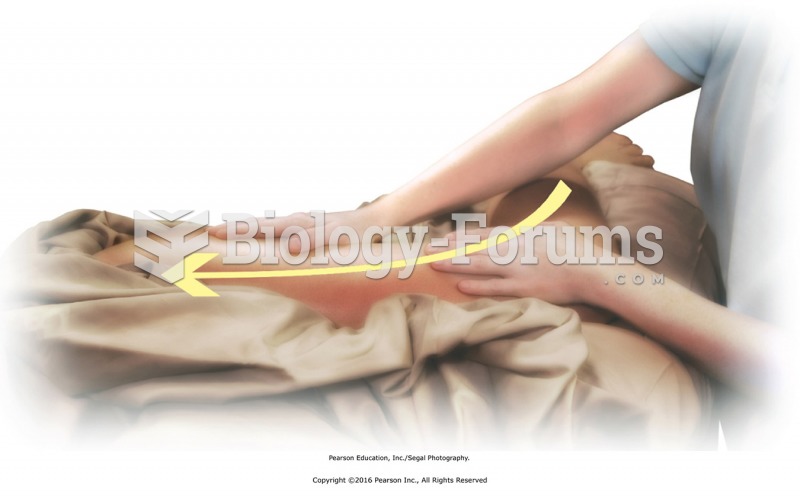
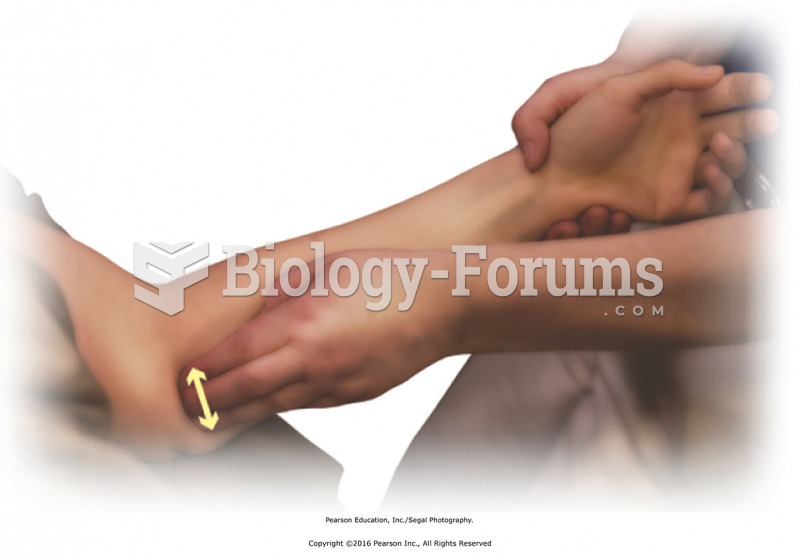 Apply friction to tendons at the elbow with thumb or fingers. Add stripping effleurage along length ...
Apply friction to tendons at the elbow with thumb or fingers. Add stripping effleurage along length ...
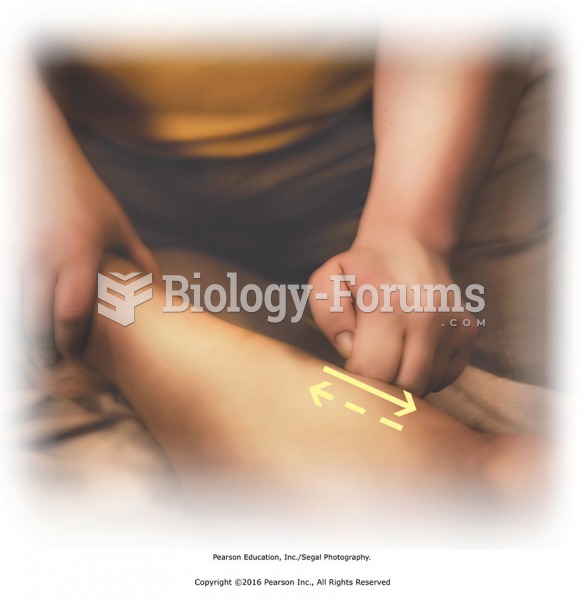 Knuckle friction to tibialis anterior. Apply superficial friction along lateral side of tibia from ...
Knuckle friction to tibialis anterior. Apply superficial friction along lateral side of tibia from ...