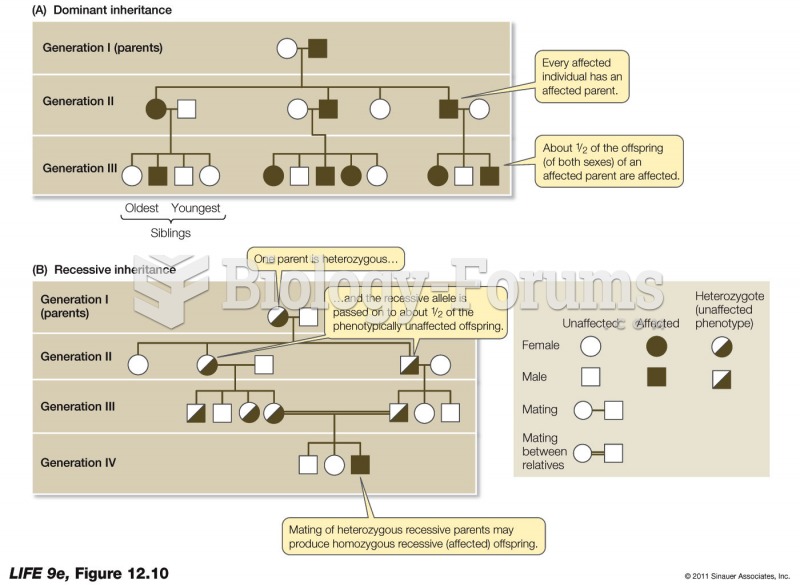
Answer to Question 1
ANS: A, E
The deciding factor in determining an adequate sample size for correlational, quasi-experimental, and experimental studies is power. Power is the capacity of the study to detect differences or relationships that actually exist in the population. Expressed another way, power is the capacity to correctly reject a null hypothesis. Often the minimum acceptable power for a study is 0.80. If a researcher does not have sufficient power to detect differences or relationships that exist in the population, one might question the advisability of conducting the study. Therefore, it is advisable to conduct the power analysis in the design phase so as to ensure an adequate sample size is obtained. One of the items required by the Institutional Review Board is a description of the subjects the researcher plans to use in the study. This includes the maximum number of subjects anticipated.
Answer to Question 2
ANS: A, E, F, G
Descriptive case studies tend to use small samples. Groups are not compared, and problems related to sampling error and generalization have little relevance for such studies. A small sample size may better serve the researcher who is interested in examining a situation in depth from various perspectives. Other descriptive studies, particularly those using survey questionnaires, and correlational studies often require large samples. In the past, quasi-experimental and experimental studies often used smaller samples than descriptive and correlational studies. The sample size increases in proportion to the number of variables included in data analysis. In quantitative research, the sample size must be large enough to identify relationships among variables or to determine differences between groups. However, in qualitative research, the focus is on the quality of information obtained from the person, situation, or event sampled versus the size of the sample. The intent is an in-depth understanding of a purposefully selected sample and not the generalization of the findings from a randomly selected sample to a target population, as in quantitative research. The number of participants in a qualitative study is adequate when saturation of information is achieved in the study area. Grounded theory and phenomenology are types of qualitative research. A pilot study is a smaller version of a proposed study conducted to develop and refine the methodology or intervention hence it uses a smaller sample size.
 The head of the jaguar is robust and the jaw extremely powerful. The size of jaguars tends to increa
The head of the jaguar is robust and the jaw extremely powerful. The size of jaguars tends to increa
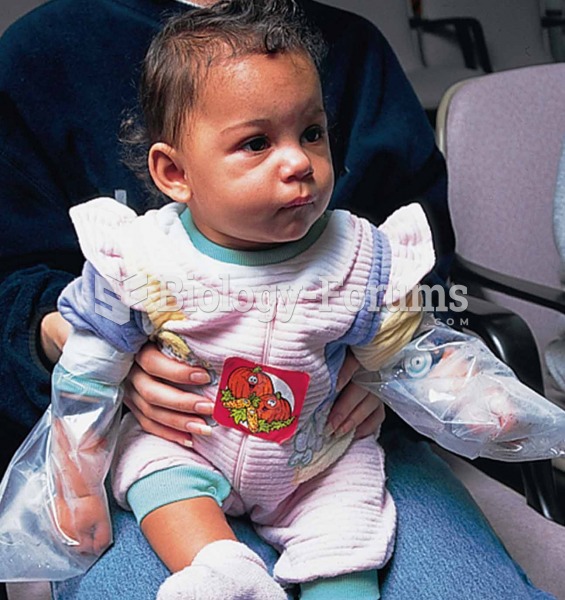 Evaluation of a child for cystic fibrosis with a sweat chloride test. Sweat is being collected under
Evaluation of a child for cystic fibrosis with a sweat chloride test. Sweat is being collected under