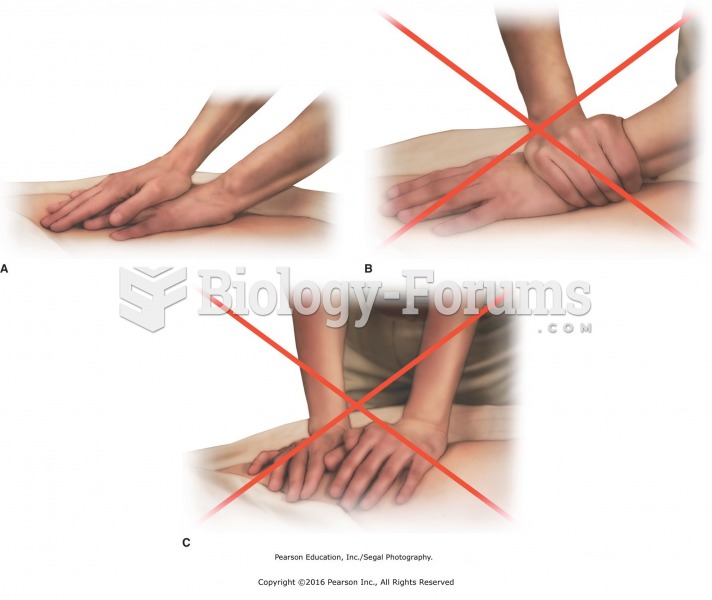
|
|
|
Approximately 15–25% of recognized pregnancies end in miscarriage. However, many miscarriages often occur before a woman even knows she is pregnant.
Prostaglandins were first isolated from human semen in Sweden in the 1930s. They were so named because the researcher thought that they came from the prostate gland. In fact, prostaglandins exist and are synthesized in almost every cell of the body.
Fewer than 10% of babies are born on their exact due dates, 50% are born within 1 week of the due date, and 90% are born within 2 weeks of the date.
Barbituric acid, the base material of barbiturates, was first synthesized in 1863 by Adolph von Bayer. His company later went on to synthesize aspirin for the first time, and Bayer aspirin is still a popular brand today.
Cucumber slices relieve headaches by tightening blood vessels, reducing blood flow to the area, and relieving pressure.